Noncanonical role of Golgi-associated macrophage TAZ in chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 39841821
- PMCID: PMC11753377
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq2395
Noncanonical role of Golgi-associated macrophage TAZ in chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis
Abstract
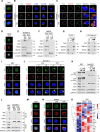
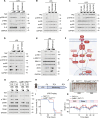
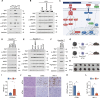
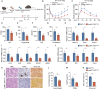
Until now, Hippo pathway-mediated nucleocytoplasmic translocation has been considered the primary mechanism by which yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) transcriptional coactivators regulate cell proliferation and differentiation via transcriptional enhanced associate domain (TEAD)-mediated target gene expression. In this study, however, we found that TAZ, but not YAP, is associated with the Golgi apparatus in macrophages activated via Toll-like receptor ligands during the resolution phase of inflammation. Golgi-associated TAZ enhanced vesicle trafficking and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in M1 macrophage independent of the Hippo pathway. Depletion of TAZ in tumor-associated macrophages promoted tumor growth by suppressing the recruitment of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Moreover, in a diet-induced metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis model, macrophage-specific deletion of TAZ ameliorated liver inflammation and hepatic fibrosis. Thus, targeted therapies being developed against YAP/TAZ-TEAD are ineffective in macrophages. Together, our results introduce Golgi-associated TAZ as a potential molecular target for therapeutic intervention to treat tumor progression and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Harvey K. F., Zhang X., Thomas D. M., The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 246–257 (2013). - PubMed

