Protective effect of ulinastatin against negative inflammatory response and organ dysfunction in acute aortic dissection surgery: The PANDA trial
- PMID: 39842406
- PMCID: PMC11866440
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101888
Protective effect of ulinastatin against negative inflammatory response and organ dysfunction in acute aortic dissection surgery: The PANDA trial
Abstract
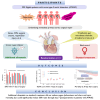
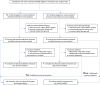
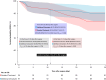
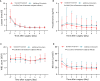
Ulinastatin is a protease-inhibiting drug with anti-inflammatory and other pharmacological properties. Little is known regarding its role following acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD) surgery. We perform a randomized controlled trial to investigate the protective effect of ulinastatin against negative inflammatory response and organ dysfunction in ATAAD surgery (PANDA). The primary outcome of mean daily Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score from baseline to 7 days of surgery is 8.80 (SD, 4.11) in the ulinastatin group and 8.61 (SD, 4.47) in the control group (mean difference between groups was 0.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], -0.24 to 0.33; p = 0.765). Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) within 7 days of surgery is lower in the ulinastatin group than in the control group (p < 0.001). Additional ulinastatin to standard treatment is likely to reduce SIRS rates instead of preventing organ dysfunction, highlighting the potential importance of the benefits of anti-inflammatory pharmacotherapeutics. The trial is registered on clinicaltrials.org (NCT04711889).
Keywords: mortality; systemic inflammatory response syndrome; type A aortic dissection; ulinastatin.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Malaisrie S.C., Szeto W.Y., Halas M., Girardi L.N., Coselli J.S., Sundt T.M., 3rd, Chen E.P., Fischbein M.P., Gleason T.G., Okita Y., et al. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery expert consensus document: Surgical treatment of acute type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021;162:735–758.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2021.04.053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

