Magnetic Resonance Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging (MR-ARFI)
- PMID: 39842847
- PMCID: PMC12179369
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.29712
Magnetic Resonance Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging (MR-ARFI)
Abstract
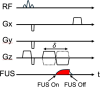
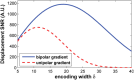
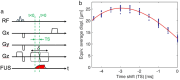
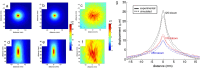
This review covers the theoretical background, pulse sequence considerations, practical implementations, and multitudes of applications of magnetic resonance acoustic radiation force imaging (MR-ARFI) described to date. MR-ARFI is an approach to encode tissue displacement caused by the acoustic radiation force of a focused ultrasound field into the phase of a MR image. The displacement encoding is done with motion encoding gradients (MEG) which have traditionally been added to spin echo-type and gradient recalled echo-type pulse sequences. Many different types of MEG (monopolar, bipolar, tripolar etc.) have been described and pros and cons are discussed. We further review studies investigating the safety of MR-ARFI, as well as approaches to simulate the MR-ARFI displacement. Lastly, MR-ARFI applications such as for focal spot localization, tissue stiffness interrogation following thermal ablation, trans-skull aberration correction, and simultaneous MR-ARFI and MR thermometry are discussed. EVIDENCE LEVEL: N/A TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 1.
Keywords: ARFI; MR‐ARFI; acoustic radiation force imaging; focused ultrasound; high intensity focused ultrasound; thermal therapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
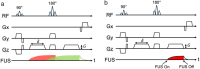


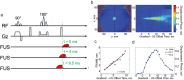

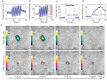
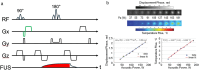

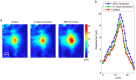

References
-
- Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, Nightingale RW, Trahey GE. On the feasibility of remote palpation using acoustic radiation force. J Acoust Soc Am 2001;110:625‐634. - PubMed
-
- Trahey GE, Palmeri ML, Bentley RC, Nightingale KR. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the mechanical properties of arteries: In vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol 2004;30:1163‐1171. - PubMed
-
- Ashikuzzaman M, Heroux A, Tang A, Cloutier G, Rivaz H. Displacement tracking techniques in ultrasound elastography: From cross correlation to deep learning. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 2024;71:842‐871. - PubMed
-
- Nakano M, Kuromatsu R, Kawaguchi T. Ultrasonographic assessment of tissue stiffness: Recent progress in transient elastography and shear wave elastography in the liver and various organs. Kurume Med J 2024;70(1.2):1‐10. - PubMed
-
- Bercoff J, Muller M, Tanter M, Fink M. Study of viscous and elastic properties of soft tissues using supersonic shear imaging. Proc IEEE Ultrason Symp 2003;1:925‐928.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R37 CA224141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA259686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA224141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB033117/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB033638/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB033638/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA259686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB028316/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB028316/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB033117/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

