Global comparison of the economic costs of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39842921
- PMCID: PMC11784380
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-084917
Global comparison of the economic costs of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, yet no comprehensive evaluation of its global economic costs exists. We conducted a systematic review with meta-analysis to examine the costs of CHD treatment by region and CHD subtypes, examine whether there are cost difference by sex, and examine costing methodologies.
Design: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of non-randomised studies.
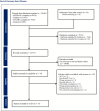
Data sources: We searched Medline, Embase, CINAHL, EconLit and Google Scholar from 1 January 2000 to February 2023.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: We included observational studies reporting economic costs of CHD treatment and outcomes for adults that were published in English.
Data extraction and synthesis: Data extraction and quality assessment were independently undertaken by two reviewers. Costs were converted to percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) per capita of corresponding country. A random-effects model was used for meta-analysis using StataSE V.18 to calculate the pooled percentage. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic. Meta-regression and bias assessment were performed.
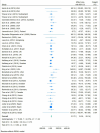
Results: Out of 20 100 records identified, 37 studies (including 2 564 189 individuals) from 22 countries were included in the qualitative synthesis and the quantitative meta-analysis. In most countries, the annual cost of CHD exceeds many times the total health expenditure per capita. The pooled direct annual cost of CHD per patient varied from 4.9% to 137.8% of GDP per capita (Int$ purchasing power parity), with pooled percentage of 21.7% (95% CI 15.3, 28.1) for those with CHD. Slight difference in the annual pooled cost of CHD was observed, with a 2% of GDP per capita higher cost in men (95% CI 0.8, 3.2). Most studies applied a top-down costing approach (n=21).
Conclusions: The review illustrates the expense associated with CHD, which is varied by region and CHD subtypes. The observed cost difference by sex warrants further exploration of sex-specific factors influencing cost disparities. Exploring advanced costing methods such as time-driven activity-based costing can optimise resource allocation and identify opportunities to reduce unnecessary costs and cost disparities.
Prospero registration number: CRD42023412044.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; HEALTH ECONOMICS; Meta-Analysis; Systematic Review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Economic burden of hypertension in Iran: a prevalence-based cost of illness study.BMJ Open. 2025 Jun 8;15(6):e099322. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-099322. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40484429 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and electronic cigarette interventions for smoking cessation in adults: component network meta-analyses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 12;9(9):CD015226. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015226.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37696529 Free PMC article.
-
The global economic burden of COVID-19 disease: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 16;13(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02476-6. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38365735 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating comparative effectiveness of psychosocial interventions adjunctive to opioid agonist therapy for opioid use disorder: A systematic review with network meta-analyses.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 28;15(12):e0244401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244401. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33370393 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing and Its Use in Health Economic Analysis: A Systematic Literature Review.Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s40258-025-00988-3. Online ahead of print. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2025. PMID: 40676406
-
Global Perspectives on Coronary Artery Disease: The Emerging Role of miRNAs.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025 Jun 17;27(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s11883-025-01309-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025. PMID: 40526174 Review.
-
The Value of Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare: A Focus on Screening and Early Detection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;15(5):648. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050648. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coronary Heart Disease. https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/heart-stroke-vascular-diseases/hsvd-fact... Available.
-
- World Heart Federation Cost of heart disease in Latin America. https://world-heart-federation.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/WHF_Econom... Available.
-
- The Economist Intelligence Unit Limited The cost of silence: cardiovascular disease in Asia. https://impact.economist.com/projects/ageing-shift/index.htmlp=3265.html... Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical