Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cell-free-DNA-based diagnostics
- PMID: 39843210
- PMCID: PMC11789496
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.278413.123
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cell-free-DNA-based diagnostics
Abstract
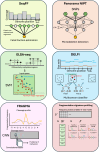
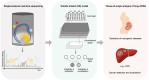
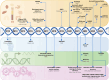
The discovery of circulating fetal and tumor cell-free DNA (cfDNA) molecules in plasma has opened up tremendous opportunities in noninvasive diagnostics such as the detection of fetal chromosomal aneuploidies and cancers and in posttransplantation monitoring. The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies makes it possible to scrutinize the characteristics of cfDNA molecules, opening up the fields of cfDNA genetics, epigenetics, transcriptomics, and fragmentomics, providing a plethora of biomarkers. Machine learning (ML) and/or artificial intelligence (AI) technologies that are known for their ability to integrate high-dimensional features have recently been applied to the field of liquid biopsy. In this review, we highlight various AI and ML approaches in cfDNA-based diagnostics. We first introduce the biology of cell-free DNA and basic concepts of ML and AI technologies. We then discuss selected examples of ML- or AI-based applications in noninvasive prenatal testing and cancer liquid biopsy. These applications include the deduction of fetal DNA fraction, plasma DNA tissue mapping, and cancer detection and localization. Finally, we offer perspectives on the future direction of using ML and AI technologies to leverage cfDNA fragmentation patterns in terms of methylomic and transcriptional investigations.
© 2025 Tsui et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Mostafa YS, Magdon-Ismail M, Lin H-T. 2012. Learning from data. AMLBook, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
