Real-world clinical multi-omics analyses reveal bifurcation of ER-independent and ER-dependent drug resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors
- PMID: 39843429
- PMCID: PMC11754447
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55914-x
Real-world clinical multi-omics analyses reveal bifurcation of ER-independent and ER-dependent drug resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors
Abstract
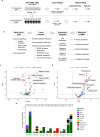
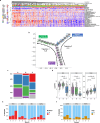
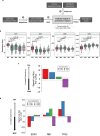
To better understand drug resistance mechanisms to CDK4/6 inhibitors and inform precision medicine, we analyze real-world multi-omics data from 400 HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapies, including 200 pre-treatment and 227 post-progression samples. The prevalences of ESR1 and RB1 alterations significantly increase in post-progression samples. Integrative clustering analysis identifies three subgroups harboring different resistance mechanisms: ER driven, ER co-driven and ER independent. The ER independent subgroup, growing from 5% pre-treatment to 21% post-progression, is characterized by down-regulated estrogen signaling and enrichment of resistance markers including TP53 mutations, CCNE1 over-expression and Her2/Basal subtypes. Trajectory inference analyses identify a pseudotime variable strongly correlated with ER independence and disease progression; and revealed bifurcated evolutionary trajectories for ER-independent vs. ER-dependent drug resistance mechanisms. Machine learning models predict therapeutic dependency on ESR1 and CDK4 among ER-dependent tumors and CDK2 dependency among ER-independent tumors, confirmed by experimental validation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing non-financial Interests but the following competing financial interests. All authors were employees of Pfizer Inc. at the time the work was performed.
Figures



References
-
- Eggersmann, T. K., Degenhardt, T., Gluz, O., Wuerstlein, R. & Harbeck, N. CDK4/6 inhibitors expand the therapeutic options in breast cancer: palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib. BioDrugs33, 125–135 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

