RNAi-based ALOX15B silencing augments keratinocyte inflammation in vitro via EGFR/STAT1/JAK1 signalling
- PMID: 39843435
- PMCID: PMC11754432
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07357-x
RNAi-based ALOX15B silencing augments keratinocyte inflammation in vitro via EGFR/STAT1/JAK1 signalling
Abstract
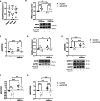
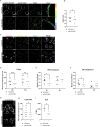
Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase type B (ALOX15B) peroxidises polyunsaturated fatty acids to their corresponding fatty acid hydroperoxides, which are subsequently reduced into hydroxy-fatty acids. A dysregulated abundance of these biological lipid mediators has been reported in the skin and blood of psoriatic compared to healthy individuals. RNAscope and immunohistochemistry revealed increased ALOX15B expression in lesional psoriasis samples. Using a cytokine cocktail containing IL-17A, interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha to produce a psoriasis-like phenotype, a role for ALOX15B in human epidermal keratinocyte inflammation was investigated. siRNA-mediated silencing of ALOX15B increased CCL2 expression and secretion. In addition to CCL2, secretion of CCL5 and CXCL10 were elevated in skin equivalents treated with lipoxygenase inhibitor ML351. Inhibition of the JAK1/STAT1 pathway reversed the enhanced CCL2 expression found with ALOX15B silencing. Previous studies have linked epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition with the upregulation of cytokines including CCL2, CCL5 and CXCL10. ALOX15B silencing reduced EGFR expression and inhibition of EGFR signalling potentiated the effect of ALOX15B silencing on increased CCL2, CCL5 and CXCL10 expression. Confirming previous findings, gene expression of cholesterol biosynthesis genes was reduced via reduced ERK phosphorylation. Reduced ERK phosphorylation was dependant on EGFR and NRF2 activation. Furthermore, plasma membrane lipids were investigated via confocal microscopy, revealing reduced cholesterol and lipid rafts. This study suggests a role for ALOX15B in keratinocyte inflammation through modulation of lipid peroxidation and the EGFR/JAK1/STAT1 signalling axis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Clinic of the Goethe-University (116/11); written, informed consent was obtained from all patients and control participants. The Declaration of Helsinki protocols were followed.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

