Efficacy and safety of first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab treatment in elderly patients (aged ≥ 75 years) with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39843575
- PMCID: PMC11754340
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-025-06089-x
Efficacy and safety of first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab treatment in elderly patients (aged ≥ 75 years) with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab (Nivo-Ipi) combination therapy is an effective first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its effectiveness and feasibility in elderly patients (aged ≥ 75 years) remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of first-line Nivo-Ipi therapy in elderly patients with NSCLC.
Methods: This retrospective study included 57 patients with NSCLC (52 men and 5 women), aged ≥ 75 years (range: 75-86) who received first-line Nivo-Ipi therapy from December 2020 to November 2022 at four institutes in Japan. Patient characteristics, therapeutic efficacy, and the incidence and severity of adverse events (AE) were assessed.
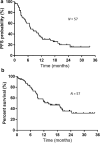
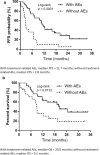
Results: The overall response rate was 42.1%, the disease control rate was 73.6%, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 7.1 months, and the median overall survival (OS) was 14.1 months. Common Grade ≥ 3 AEs included pneumonitis, elevated aspartate transaminase, elevated alanine transaminase, adrenal insufficiency, and colitis. No treatment-related deaths were reported. PFS and OS were longer in patients who experienced treatment-related AEs. Patients with and without AEs had a median PFS of 11.7 and 2.8 months, respectively. Similarly, the median OS of patients with and without AEs was 20.4 and 9.0 months, respectively.
Conclusion: First-line Nivo-Ipi therapy is effective in elderly patients with NSCLC. Although there was an increased incidence of pneumonitis, the treatment was manageable and presented as a viable treatment option. Notably, the occurrence of treatment-related AEs was associated with improved clinical outcomes, suggesting a potential prognostic value of AEs in this population.
Keywords: Advanced non-small cell lung cancer; Elderly patients; First-line treatment; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Ipilimumab; Nivolumab.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics Approval: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Institutional Review Board of the International Medical Center, Saitama Medical University (number 2023-080). Consent to participate: The need for informed consent was waived by the institutional review boards of the participating institutions owing to the retrospective nature of the study. However, an opportunity to refuse participation through the opt-out method was provided. Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

