Improving the odds of survival: transgenerational effects of infections
- PMID: 39843630
- PMCID: PMC11982362
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00192-9
Improving the odds of survival: transgenerational effects of infections
Abstract
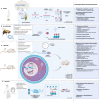
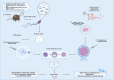
Recent studies argue for a novel concept of the role of chromatin as a carrier of epigenetic memory through cellular and organismal generations, defining and coordinating gene activity states and physiological functions. Environmental insults, such as exposures to unhealthy diets, smoking, toxic compounds, and infections, can epigenetically reprogram germ-line cells and influence offspring phenotypes. This review focuses on intergenerational and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in different plants, animal species and humans, presenting the up-to-date evidence and arguments for such effects in light of Darwinian and Lamarckian evolutionary theories. An overview of the epigenetic changes induced by infection or other immune challenges is presented, and how these changes, known as epimutations, contribute to shaping offspring phenotypes. The mechanisms that mediate the transmission of epigenetic alterations via the germline are also discussed. Understanding the relationship between environmental fluctuations, epigenetic changes, resistance, and susceptibility to diseases is critical for unraveling disease etiology and adaptive evolution.
Keywords: Epigenetic Memory; Epigenetics; Evolution; Infections; Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. MGN is a scientific founder of TTxD, Lemba, Salvina and Biotrip. MGN is an editorial advisory board member. This has no bearing on the editorial consideration of this article for publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
-
Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of sperm epimutations promote genetic mutations.Epigenetics. 2015;10(8):762-71. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1062207. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26237076 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Obesity Susceptibility.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul;31(7):478-494. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2020.02.009. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32521235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational Inheritance of Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Alterations during Mammalian Development.Cells. 2019 Dec 3;8(12):1559. doi: 10.3390/cells8121559. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31816913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease.Environ Epigenet. 2018 Jul 17;4(2):dvy016. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvy016. eCollection 2018 Apr. Environ Epigenet. 2018. PMID: 30038800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T (2016) The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat Rev Genet 17:487–500 - PubMed
-
- Almond D (2006) Is the 1918 influenza pandemic over? Long-term effects of in utero influenza exposure in the post-1940 U.S. population. J Political Econ 114:672–712
-
- Almond D, Mazumder B (2005) The 1918 influenza pandemic and subsequent health outcomes: an analysis of SIPP data. Am Econ Rev 95:258–262 - PubMed
-
- Arber W (2008) Molecular mechanisms driving Darwinian evolution. Math Comput Model 47:666–674
-
- Balhorn R, Gledhill BL, Wyrobek AJ (1977) Mouse sperm chromatin proteins: quantitative isolation and partial characterization. Biochemistry 16:4074–4080 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

