Empowering PET imaging reporting with retrieval-augmented large language models and reading reports database: a pilot single center study
- PMID: 39843863
- PMCID: PMC12119711
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-025-07101-9
Empowering PET imaging reporting with retrieval-augmented large language models and reading reports database: a pilot single center study
Abstract
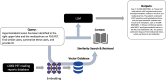
Purpose: The potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in enhancing a variety of natural language tasks in clinical fields includes medical imaging reporting. This pilot study examines the efficacy of a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) LLM system considering zero-shot learning capability of LLMs, integrated with a comprehensive database of PET reading reports, in improving reference to prior reports and decision making.
Methods: We developed a custom LLM framework with retrieval capabilities, leveraging a database of over 10 years of PET imaging reports from a single center. The system uses vector space embedding to facilitate similarity-based retrieval. Queries prompt the system to generate context-based answers and identify similar cases or differential diagnoses. From routine clinical PET readings, experienced nuclear medicine physicians evaluated the performance of system in terms of the relevance of queried similar cases and the appropriateness score of suggested potential diagnoses.
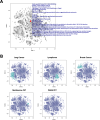
Results: The system efficiently organized embedded vectors from PET reports, showing that imaging reports were accurately clustered within the embedded vector space according to the diagnosis or PET study type. Based on this system, a proof-of-concept chatbot was developed and showed the framework's potential in referencing reports of previous similar cases and identifying exemplary cases for various purposes. From routine clinical PET readings, 84.1% of the cases retrieved relevant similar cases, as agreed upon by all three readers. Using the RAG system, the appropriateness score of the suggested potential diagnoses was significantly better than that of the LLM without RAG. Additionally, it demonstrated the capability to offer differential diagnoses, leveraging the vast database to enhance the completeness and precision of generated reports.
Conclusion: The integration of RAG LLM with a large database of PET imaging reports suggests the potential to support clinical practice of nuclear medicine imaging reading by various tasks of AI including finding similar cases and deriving potential diagnoses from them. This study underscores the potential of advanced AI tools in transforming medical imaging reporting practices.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Large language model; PET reports; Retrieval-augmented generation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: H.C. is a co-founder of Portrai. Ethics approval: The retrospective analysis of human data and the waiver of informed consent were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Seoul National University Hospital (No. 2401-090-1501). Consent to participate: Written informed consent was acquired from all patients. Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures


References
-
- Elkassem AA, Smith AD. Potential use cases for ChatGPT in radiology reporting. Am J Roentgenol. 2023. - PubMed
-
- Doshi R, Amin K, Khosla P, Bajaj S, Chheang S, Forman HP. Utilizing Large Language Models to Simplify Radiology Reports: a comparative analysis of ChatGPT3. 5, ChatGPT4. 0, Google Bard, and Microsoft Bing. medRxiv. 2023:2023.06. 04.23290786.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

