Microglia modulate the cerebrovascular reactivity through ectonucleotidase CD39
- PMID: 39843911
- PMCID: PMC11754601
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56093-5
Microglia modulate the cerebrovascular reactivity through ectonucleotidase CD39
Abstract
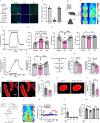
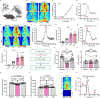
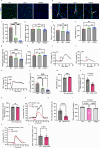
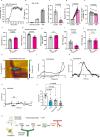
Microglia and the border-associated macrophages contribute to the modulation of cerebral blood flow, but the mechanisms have remained uncertain. Here, we show that microglia regulate the cerebral blood flow baseline and the responses to whisker stimulation or intra-cisternal magna injection of adenosine triphosphate, but not intra-cisternal magna injection of adenosine in mice model. Notably, microglia repopulation corrects these cerebral blood flow anomalies. The microglial-dependent regulation of cerebral blood flow requires the adenosine triphosphate-sensing P2RY12 receptor and ectonucleotidase CD39 that initiates the dephosphorylation of extracellular adenosine triphosphate into adenosine in both male and female mice. Pharmacological inhibition or CX3CR1-CreER-mediated deletion of CD39 mimics the cerebral blood flow anomalies in microglia-deficient mice and reduces the upsurges of extracellular adenosine following whisker stimulation. Together, these results suggest that the microglial CD39-initiated breakdown of extracellular adenosine triphosphate co-transmitter is an important step in neurovascular coupling and the regulation of cerebrovascular reactivity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.C.R. is a scientific founder of Purinomia Biotech Inc and has consulted for eGenesis and SynLogic Inc; his interests are reviewed and managed by HMFP, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center by the institutional conflict-of-interest policies. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lassen, N. A. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in man. Physiol. Rev.39, 183–238 (1959). - PubMed
-
- Berne, R. M., Winn, H. R. & Rubio, R. The local regulation of cerebral blood flow. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis.24, 243–260 (1981). - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio, M. P., Burnstock, G., Verkhratsky, A. & Zimmermann, H. Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci.32, 19–29 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res.120, 207–228 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG072489/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS108763/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS121014/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS125677/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- F31 AG074652/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS127392/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS125788/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- RF1 AG068558/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH118329/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS135693/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS125788/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS127392/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 NS125677/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL167511/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA047233/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD109025/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068558/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094400/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS106721/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG065923/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

