Non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals are toxic against Escherichia coli with no evolution of cross-resistance to antibiotics
- PMID: 39843932
- PMCID: PMC11721113
- DOI: 10.1038/s44259-024-00028-5
Non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals are toxic against Escherichia coli with no evolution of cross-resistance to antibiotics
Abstract
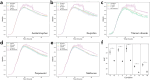
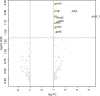
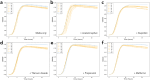
Antimicrobial resistance can arise in the natural environment via prolonged exposure to the effluent released by manufacturing facilities. In addition to antibiotics, pharmaceutical plants also produce non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals, both the active ingredients and other components of the formulations. The effect of these on the surrounding microbial communities is less clear. We aimed to assess whether non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals and other compounds produced by pharmaceutical plants have inherent toxicity, and whether long-term exposure might result in significant genetic changes or select for cross-resistance to antibiotics. To this end, we screened four non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals (acetaminophen, ibuprofen, propranolol, metformin) and titanium dioxide for toxicity against Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 and conducted a 30 day selection experiment to assess the effect of long-term exposure. All compounds reduced the maximum optical density reached by E. coli at a range of concentrations including one of environmental relevance, with transcriptome analysis identifying upregulated genes related to stress response and multidrug efflux in response ibuprofen treatment. The compounds did not select for significant genetic changes following a 30 day exposure, and no evidence of selection for cross-resistance to antibiotics was observed for population evolved in the presence of ibuprofen in spite of the differential gene expression after exposure to this compound. This work suggests that these compounds, at environmental concentrations, do not select for cross-resistance to antibiotics in E. coli.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: An author of this publication, Jessica M. A. Blair, is also the current Editor-in-Chief of npj Antimicrobials and Resistance. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Laxminarayan, R. et al. Access to effective antimicrobials: a worldwide challenge. The Lancet387, 168–175 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Fick, J. et al. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.28, 2522–7 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lin, A. Y. C. & Tsai, Y. T. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in Taiwan’s surface waters: Impact of waste streams from hospitals and pharmaceutical production facilities. Sci. Total Environ.407, 3793–3802 (2009). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

