Profile and resistance levels of 136 integron resistance genes
- PMID: 39843947
- PMCID: PMC11721406
- DOI: 10.1038/s44259-023-00014-3
Profile and resistance levels of 136 integron resistance genes
Abstract
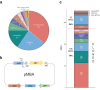
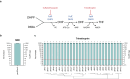
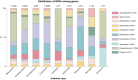
Integrons have played a major role in the rise and spread of multidrug resistance in Gram-negative pathogens and are nowadays commonplace among clinical isolates. These platforms capture, stockpile, and modulate the expression of more than 170 antimicrobial resistance cassettes (ARCs) against most clinically-relevant antibiotics. Despite their importance, our knowledge on their profile and resistance levels is patchy, because data is scattered in the literature, often reported in different genetic backgrounds and sometimes extrapolated from sequence similarity alone. Here we have generated a collection of 136 ARCs against 8 antibiotic families and disinfectants. Cassettes are cloned in a vector designed to mimic the genetic environment of a class 1 integron, and transformed in Escherichia coli. We have measured the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) to the most relevant molecules from each antibiotic family. With more than 500 MIC values, we provide an exhaustive and comparable quantitation of resistance conferred by ARCs. Our data confirm known resistance trends and profiles while revealing important differences among closely related genes. We have also detected genes that do not confer the expected resistance, to the point of challenging the role of the whole family of qac genes in resistance against disinfectants. Our work provides a detailed characterization of integron resistance genes at-a-glance.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- O´Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Chaired b by J O’Neil, and supported by the Wellcome Trust and the UK Government. (2014).
-
- Mitshuhashi, S., Harada, K., Hashimoto, H. & Egawa, R. On the drug-resistance of enteric bacteria. 4. Drug-resistance of Shigella prevalent in Japan. Jpn J. Exp. Med.31, 47–52 (1961). - PubMed
-
- Escudero JA, Loot C, Nivina A, Mazel. D. The integron: Adaption on demand. Microbiol. Spectr. 10.1128/microbiolspec (2014). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

