Unlocking the potential of experimental evolution to study drug resistance in pathogenic fungi
- PMID: 39843963
- PMCID: PMC11721431
- DOI: 10.1038/s44259-024-00064-1
Unlocking the potential of experimental evolution to study drug resistance in pathogenic fungi
Abstract
Exploring the dynamics and molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial drug resistance provides critical insights for developing effective strategies to combat it. This review highlights the potential of experimental evolution methods to study resistance in pathogenic fungi, drawing on insights from bacteriology and innovative approaches in mycology. We emphasize the versatility of experimental evolution in replicating clinical and environmental scenarios and propose that incorporating evolutionary modelling can enhance our understanding of antifungal resistance evolution. We advocate for a broader application of experimental evolution in medical mycology to improve our still limited understanding of drug resistance in fungi.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

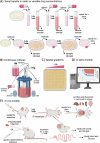

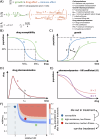
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

