Isolation, characterization and therapeutic efficacy of lytic bacteriophage ZK22 against Salmonella Typhimurium in mice
- PMID: 39844042
- PMCID: PMC11753042
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-025-03772-4
Isolation, characterization and therapeutic efficacy of lytic bacteriophage ZK22 against Salmonella Typhimurium in mice
Abstract
Background: Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is one of the most common serovars of Salmonella associated with clinical cases. It not only leads to diarrhea and mortality raised in livestock and poultry farming, but also poses a risk to food safety.
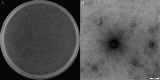
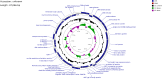
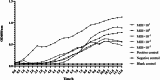
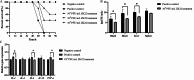
Results: In this study, a lytic bacteriophage named ZK22 was isolated and identified from sewage. It exhibited favorable capability against 20 strains of S. Typhimurium. The genome of ZK22 consisted of a double-stranded DNA with a total length of 47,066 base pairs and a GC content of 45.71%. A total of 78 coding sequences were predicted, with no virulence genes or drug resistance genes predicted. Based on blastn similarity analysis, ZK22 belongs to the genus Skatevirus of the class Caudoviricetes, as a long-tailed Siphovirus. Biological characteristics of ZK22 indicated that the optimal multiplicity of infection (MOI) of bacteriophage ZK22 to S. Typhimurium was 10- 2 (PFU/cell), with an incubation period of around 10 min and the burst size of 393 PFU/cell. The physicochemical resistance results of ZK22 demonstrated that it maintained stability under temperatures ranging from 4 °C to 70 °C and under pH conditions ranging from 3 to 12. After inoculating S. Typhimurium at 37 °C, co-culture mixed with the optimal multiplicity of infection exhibited the lowest OD600 within 12 h, demonstrating the exceptional antibacterial effect. Inoculation of phage ZK22 in mice infected with S. Typhimurium was performed to assess its therapeutic efficacy in vivo. The results showed that phage ZK22 at a dose of 108 PFU/mL increased the survival rates of infected mice, effectively suppressed the dissemination and colonization of the host bacteria in the mice, and alleviated the inflammatory response caused by the infection.
Conclusions: In summary, bacteriophage ZK22 presents favorable application prospects as a potential biological agent for the control of Salmonella infections in livestock and poultry farming.
Keywords: Salmonella Typhimurium; Antibacterial effect; Biological agent; Lytic bacteriophage; Therapeutic efficacy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal study protocol was approved by approval of the Animal Management and Ethics Committee of the Zhongkai University of Agricultural Engineering (ethical approval number: ZHKUMO-2023-043). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

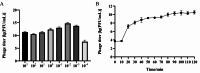
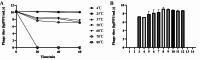
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

