Purine-rich element binding protein alpha: a DNA/RNA binding protein with multiple roles in cancers
- PMID: 39844051
- PMCID: PMC11755881
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01087-8
Purine-rich element binding protein alpha: a DNA/RNA binding protein with multiple roles in cancers
Abstract
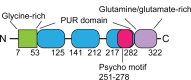
Proteins that bind to DNA/RNA are typically evolutionarily conserved with multiple regulatory functions in transcription initiation, mRNA translation, stability of RNAs, and RNA splicing. Therefore, dysregulation of DNA/RNA binding proteins such as purine-rich element binding protein alpha (PURα) disrupts signaling transduction and often leads to human diseases including cancer. PURα was initially recognized as a tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and prostate cancer (PC). Most recently, several studies have revealed that PURα is dysregulated in multiple cancers, such as breast cancer (BC) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The oncogenic or tumor-suppressive functions of PURα are realized via regulating RNA/protein interaction, mRNA translation, formation of stress granules (SGs), and transcriptional regulation of several oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Although DNA/RNA binding proteins are hardly targeted, novel strategies have been applied to identify compounds targeting PURα and have demonstrated promising anti-tumor efficacy in the preclinical study. The present review summarizes the most recently discovered critical roles of PURα in various cancer types, providing an overview of the biomarker and therapeutic target potential of PURα for patients with cancer.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; DNA/RNA binding protein; PURα.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 137012751/YangZhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau
- 23KJD310006/Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- 82403939/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82303977/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20240923/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

