Real-world short-term outcomes and treatment regimen comparisons in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line immune combinations
- PMID: 39844084
- PMCID: PMC11752628
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-13504-6
Real-world short-term outcomes and treatment regimen comparisons in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line immune combinations
Abstract
Background: Immune-combinations have recently become the standard first-line treatment for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). This study evaluated the applicability of the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) risk model in predicting outcomes for patients treated with either immune-oncologic drug doublet (IO-IO) or immune-oncologic drug tyrosine kinase inhibitor combinations (IO-TKI). A secondary objective to compare the effectiveness of IO-IO versus IO-TKI within the IMDC risk groups over a short follow-up period.
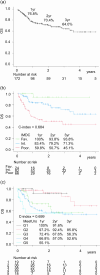
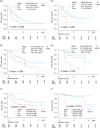
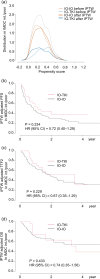
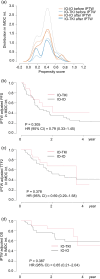
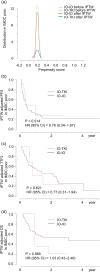
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 172 patients with mRCC treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations. Progression free survival (PFS), time to treatment failure 2 (TTF2), and overall survival (OS) were compared between IMDC risk categories. Model fit was assessed using the c-index. The inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) method was used to adjust and compare outcomes between IO-IO and IO-TKI, except for IMDC favorable risk patients due to the small number of IO-IO cases.
Results: The IMDC risk model demonstrated a c-index of 0.684 (OS) for entire cohort, 0.600 (PFS), 0.596 (TTF2), and 0.624 (OS) for IO-IO, and 0.667 (PFS), 0.702 (TTF2), and 0.751 (OS) for IO-TKI. In the IMDC intermediate and poor risk groups after IPTW adjustment, PFS (HR 0.72), TTF2 (HR 0.67), and OS (HR 0.74) did not significantly differ between IO-IO and IO-TKI. Specifically, in the IMDC intermediate risk group, PFS (HR 0.79), TTF2 (HR 0.69), and OS (HR 0.65) were longer in IO-TKI, though the differences were not statistically significant. In the IMDC poor risk group, PFS (HR 0.76), TTF2 (HR 0.77), and OS (HR 1.03) were comparable.
Conclusions: The impact of IMDC risk model on survival was modest in IO-IO, while remained statistically substantial in IO-TKI. Survival outcomes did not significantly differ between IO-IO and IO-TKI during the short follow-up period.
Keywords: Comparison; Immune-combinations; Immunotherapy; Prognosis; Renal cell carcinoma; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Ethics Committee of Hokkaido University approved this study (Approval no, 023–0105). Informed consent was waved by using the opt-out method for this retrospective study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Sei Naito received honoraria from Pfizer Japan Inc., Merk biopharma Japan Inc., Bristol Meier’s squibb Japan Inc., Ono Pharma, MSD Japan, and Eisai Co. as their sponsored speaker. Takahiro Osawa received honoraria from MSD Japan. Nobuo Shinohara received honoraria from Pfizer, Ono, BMS, MSD, Takeda, Novartis, Eisai, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Astellas, as their sponsored speaker and research funds from Ono and Takeda. Tomonori Habuchi received honoraria from Astellas, Ono, Janssen, as their sponsored speaker, and research funds from Sysmex and Mochida. Norihiko Tsuchiya received honoraria from Pfizer Japan Inc. Janssen, Novartis, Ono, Bayer, Sanofi, Takeda Pharm, Bristol-Myers Squibb Japan, and Astelas Pharma., as their sponsored speaker and research funds from Pfizer Japan Inc. and Eisai outside the submitted work. The other authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparing Immuno-oncology Combination Therapy With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2025 Jan;45(1):379-386. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17426. Anticancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39740850
-
First-line immune-based combinations or sunitinib in favorable-risk metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a real-world retrospective comparison from the ARON-1 study.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 Jan 3;74(2):65. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03897-x. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 39752009 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world Outcome of Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Intermediate- or Poor-risk International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Criteria Treated by Immune-oncology Combinations: Differential Effectiveness by Risk Group?Eur Urol Oncol. 2024 Feb;7(1):102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37481365
-
Combination therapies in patients with favorable risk metastatic renal cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2024 Jan;122:102667. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102667. Epub 2023 Dec 10. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024. PMID: 38101099
-
Efficacy of VEGFR-TKIs plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with favorable IMDC prognosis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Nov;100:102295. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102295. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34564043 Review.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, McDermott DF, Escudier B, Burotto M, Choueiri TK, Hammers HJ, Barthélémy P, Plimack ER, Porta C, George S, et al. Conditional survival and long-term efficacy with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2022;128(11):2085–97. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Haanen J, Campbell MT, Venugopal B, Kollmannsberger C, Gravis-Mescam G, Uemura M, Lee JL, et al. Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(8):1030–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Plimack ER, Powles T, Stus V, Gafanov R, Nosov D, Waddell T, Alekseev B, Pouliot F, Melichar B, Soulières D, et al. Pembrolizumab Plus Axitinib Versus Sunitinib as First-line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: 43-month Follow-up of the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 Study. Eur Urol. 2023;84(5):449–54. - PubMed
-
- Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Apolo AB, Bourlon MT, Shah AY, Suárez C, Porta C, Barrios CH, Richardet M, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up from the phase III randomised CheckMate 9ER trial. ESMO open. 2024;9(5):102994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T, Grünwald V, Hutson TE, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Merchan J, Goh JC, et al. Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Sunitinib in First-Line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Prespecified Overall Survival Analysis of CLEAR, a Phase III Study. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(11):1222–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

