Factors associated with dental care utilization among Iranian adult populations based on Anderson model
- PMID: 39844135
- PMCID: PMC11755850
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-21540-x
Factors associated with dental care utilization among Iranian adult populations based on Anderson model
Abstract
Background: The utilization of dental care is affected by different factors. Despite the importance of dental care, there are significant disparities in its utilization among various population groups. The aim of this study was to identify the main factors of dental care utilization and the influences of the Health Transformation Plan (HTP) in Iran based on the Anderson model.
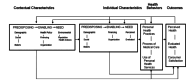
Methods and materials: This cross-sectional house-by-house study was conducted during Aug-Nov 2022 among 704 adult people in two cities under the coverage of the HTP and two cities out-side the plan using a multi-stage sampling method. Dental visit in the last year was considered as the utilization of the dental services. Independent Factors included the contextual, individual enabling, individual predisposing and individual need factors based on the Andersen model. Personal health behaviors were also assessed. Statistical analysis was conducted using Chi-square tests, simple and multivariable logistic regression models (α < 0.05).
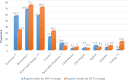
Results: The 63.1% of the participants covered by the HTP and 57.7% of the population outside the plan sought dental care in the past year. In the final model individuals in the 35-44 age group (OR = 1.5, 95% CI = 1.02-2.2), males (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 1.2-2.5), single individuals (OR = 1.4, 95% CI = 1.01-2) and those with the perception of need for dental treatment (OR = 2.1, 95% CI = 1.3-3.4) had higher chance of dental visit. Better perceived oral health status was associated with lower chance of visiting the dentist (OR = 0.9, 95% CI = 0.8-0.9). Being covered by the HTP was not significantly in association with the chance of dental visit in the last year (p value = 0.19, OR = 0.78, 95%CI = 0.55-1.12).
Conclusion: The predisposing factors including age, gender, marital status, and perceived oral health status and perceptions of dental need were the main factors in association with the dental utilization behavior among adults and the coverage by the HTP did not have significant effect on it.
Keywords: Dental health services; Health care reform; Health policy; Iran; Services utilization.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was done in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration ( http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/b3/index.html ) and protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee in the Vice Chancellery of Research at the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (IR.MUI.RESARCH.REC.1400.383). In addition, the necessary permits and approvals to enter homes in the respective areas were obtained from municipalities and other related governmental organizations and in each house, the investigators (one examiner and an assistant) offered the permits. The informed written consent was obtained from all of the participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preventive and curative dental services utilization among children aged 12 years and younger in Tehran, Iran, based on the Andersen behavioral model: A generalized structural equation modeling.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 16;20(1):e0312043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312043. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39820811 Free PMC article.
-
Dental health-care service utilisation and its determinants in West Iran: a cross-sectional study.Int Dent J. 2018 Jun;68(3):176-182. doi: 10.1111/idj.12346. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Int Dent J. 2018. PMID: 29171015 Free PMC article. English.
-
Predictors of dental care utilization among working poor Canadians.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2009 Jun;37(3):199-208. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2009.00471.x. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19508268
-
Socioeconomic inequalities in the utilization of dental services among adults in Saudi Arabia.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Apr 21;22(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02162-w. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35448991 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of dental care among adult populations: a scoping review of applied models.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Aug 27;23(1):596. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03323-1. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37635224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petersen PE. World Health Organization global policy for improvement of oral health-World Health Assembly 2007. Int Dent J. 2008;58(3):115–21. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi M, Zamani M, Ganjbakhsh M. Justice in medical ethics. Med Ethics. 2010;3(10):11–33.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

