Glutamine Synthetase: Diverse Regulation and Functions of an Ancient Enzyme
- PMID: 39844577
- PMCID: PMC11800386
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00763
Glutamine Synthetase: Diverse Regulation and Functions of an Ancient Enzyme
Abstract
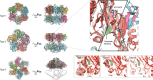
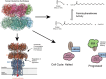
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is a ubiquitous enzyme central to nitrogen metabolism, catalyzing the ATP-dependent formation of glutamine from glutamate and ammonia. Positioned at the intersection of nitrogen metabolism with carbon metabolism, the activity of GS is subject to sophisticated regulation. While the intricate regulatory pathways that govern Escherichia coli GS were established long ago, recent work has demonstrated that homologues are controlled by multiple distinct regulatory patterns, such as the metabolite induced oligomeric state formation in archaeal GS by 2-oxoglutarate. Such work was enabled in large part by advances in cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) that allowed greater structural access to this large enzyme complex, such as assessment of the large heterogeneous oligomeric states of GS and protein-interactor-GS complexes. This perspective highlights recent advances in understanding GS regulation, focusing on the dynamic interplay between its oligomeric state, metabolite binding, and protein interactors. These interactions modulate GS activity, influencing cellular processes such as nitrogen assimilation, carbon metabolism, and stress responses. Furthermore, we explore the emerging concept of GS "moonlighting" functions, revealing its roles in palmitoylation, cell cycle regulation, and ion channel modulation. These diverse functions highlight a newfound versatility of GS beyond its primary catalytic role and suggest complex roles in health and disease that warrant further study.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society. This publication is licensed under CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- dos Santos Moreira C. D.; Ramos M. J. R. N.; Fernandes P. M. A. A. Glutamine Synthetase Structure-catalysis Relationship—Recent Advances and Applications. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2019, 9 (4), e139910.1002/wcms.1399. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

