Levosimendan for sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: friend or foe?
- PMID: 39844909
- PMCID: PMC11752121
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1520596
Levosimendan for sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: friend or foe?
Abstract
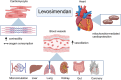
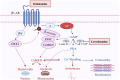
Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) involves reversible myocardial dysfunction. The use of inotropes can restore adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion, but conventional inotropes, such as dobutamine and adrenaline, have limited efficacy in such situations. Levosimendan is a novel inotrope that acts in a catecholamine-independent manner. However, study results regarding the treatment of SIMD with levosimendan are inconsistent, and the use of levosimendan is highly controversial. In this review, we summarized the therapeutic mechanisms of levosimendan in SIMD and considered recent research on how to improve the efficacy of levosimendan in SIMD. We also analyzed the potential and limitations of levosimendan for the treatment of SIMD to provide ideas for future clinical trials and the clinical application of levosimendan in SIMD.
Keywords: inotropes; levosimendan; organ protection; sepsis; sepsis-induced myocardial cardiac dysfunction.
© 2025 Du, Xiong, Hou, Yu and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levosimendan restores both systolic and diastolic cardiac performance in lipopolysaccharide-treated rabbits: comparison with dobutamine and milrinone.Crit Care Med. 2007 May;35(5):1376-82. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000261889.18102.84. Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17414729
-
Levosimendan, a new calcium-sensitizing inotrope for heart failure.Pharmacotherapy. 2004 Oct;24(10):1366-84. doi: 10.1592/phco.24.14.1366.43145. Pharmacotherapy. 2004. PMID: 15628834 Review.
-
Levosimendan versus dobutamine for sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 13;11(1):20333. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99716-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34645892 Free PMC article.
-
Inodilators in septic shock: should these be used?Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jun;8(12):796. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.04.43. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32647721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Outcome of Sepsis-induced Myocardial Dysfunction in Children with 'Sepsis' 'With' and 'Without Shock'-A Prospective Observational Study.J Trop Pediatr. 2018 Dec 1;64(6):501-509. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmx105. J Trop Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29304220
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

