Large Language Models in Healthcare: A Bibliometric Analysis and Examination of Research Trends
- PMID: 39844924
- PMCID: PMC11750729
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S502351
Large Language Models in Healthcare: A Bibliometric Analysis and Examination of Research Trends
Abstract
Background: The integration of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare has generated significant interest due to their potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, personalization of treatment, and patient care efficiency.
Objective: This study aims to conduct a comprehensive bibliometric analysis to identify current research trends, main themes and future directions regarding applications in the healthcare sector.
Methods: A systematic scan of publications until 08.05.2024 was carried out from an important database such as Web of Science.Using bibliometric tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace, we analyzed data covering publication counts, citation analysis, co-authorship, co- occurrence of keywords and thematic development to map the intellectual landscape and collaborative networks in this field.
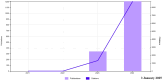
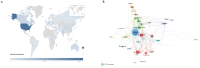
Results: The analysis included more than 500 articles published between 2021 and 2024. The United States, Germany and the United Kingdom were the top contributors to this field. The study highlights that neural network applications in diagnostic imaging, natural language processing for clinical documentation, and patient data in the field of general internal medicine, radiology, medical informatics, health care services, surgery, oncology, ophthalmology, neurology, orthopedics and psychiatry have seen significant growth in publications over the past two years. Keyword trend analysis revealed emerging sub-themes such as clinical research, artificial intelligence, ChatGPT, education, natural language processing, clinical management, virtual reality, chatbot, indicating a shift towards addressing the broader implications of LLM application in healthcare.
Conclusion: The use of LLM in healthcare is an expanding field with significant academic and clinical interest. This bibliometric analysis not only maps the current state of the research, but also identifies important areas that require further research and development. Continued advances in this field are expected to significantly impact future healthcare applications, with a focus on increasing the accuracy and personalization of patient care through advanced data analytics.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chatbot; clinical applications; diagnosis; healthcare; large language models; treatment recommendations.
© 2025 Gencer and Gencer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no personal relationships or financial interests that could seem to have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Mann B, Ryder N, Subbiah M, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:200514165. 2020
-
- Radford A, Wu J, Child R, Luan D, Amodei D, Sutskever I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog. 2019;1(8):9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

