A comprehensive review of the neurological effects of anethole
- PMID: 39844944
- PMCID: PMC11750503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.012
A comprehensive review of the neurological effects of anethole
Abstract
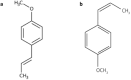
Since ancient times many countries have employed medicinal plants as part of traditional medicine. Anethole is a substance found in various plants and has two isomers, cis-anethole (CA) and trans-anethole (TA). Currently, the food industry extensively use anethole as an aromatic and flavoring component. Extensive scientific research are warranted to provide scientific proof for the usage of anethole, given its widespread use and affordable price. Preclinical studies have suggested several pharmacological effects for anethole including neuroprotective properties. It has been determined that anethole through modulation of monoamines, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic and glutamatergic neurotransmissions as well as its possible anti-inflammatory and antioxidative stress properties affected central nervous system (CNS). In this concept previous studies have demonstrated anxiolytic, antidepressant, antinociceptive, anticonvulsant, and memory improvement effects for anethole. To fully understand its therapeutic potentials, more research are required to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which TA and CA affected CNS. This review summarizes the current knowledge on pharmacological activities of the anethole concentrating its neurological properties, and the possible mechanisms underlying these effects. Various pharmacological effects which have been reported suggesting that anethole could be considered as a potential agent for management of neurological disorders.
Keywords: Anethole; Anti-inflammatory effects; Anti-oxidant properties; Nervous system; Therapeutic use.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare regarding the study described in this article and preparation of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anethole as a promising antidepressant for maternal separation stress in mice by modulating oxidative stress and nitrite imbalance.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 2;14(1):7766. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57959-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38565927 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of fennel, and its major component trans-anethole against social isolation induced behavioral deficits in rats.Physiol Int. 2020 Mar;107(1):30-39. doi: 10.1556/2060.2020.00012. Physiol Int. 2020. PMID: 32491286
-
Trans-Anethole Alleviates Trimethyltin Chloride-Induced Impairments in Long-Term Potentiation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 6;14(7):1422. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071422. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890317 Free PMC article.
-
Anethole and Its Role in Chronic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;929:247-267. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41342-6_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27771928 Review.
-
Medicinal plants used in traditional Mayan medicine for the treatment of central nervous system disorders: An overview.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114746. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114746. Epub 2021 Oct 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34656668
Cited by
-
Synergistic Larvicidal and Pupicidal Effects of Monoterpene Mixtures Against Aedes aegypti with Low Toxicity to Guppies and Honeybees.Insects. 2025 Jul 18;16(7):738. doi: 10.3390/insects16070738. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40725368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A beed A.H., Al-Huqail A.A., Albalawi S., Alghamdi S.A., Ali B., Alghanem S.M., El-Mahdy M.T. Calcium nanoparticles mitigate severe salt stress in Solanum lycopersicon by instigating the antioxidant defense system and renovating the protein profile. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023;161:36–52.
-
- Al Rouq F., El Eter E. PPAR-γ activator induces neuroprotection in hypercholesterolemic rats subjected to global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: In vivo and in vitro inhibition of oxidative stress. Exp. Gerontol. 2014;51:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Al-Harbi M.M., Qureshi S., Raza M., Ahmed M.M., Giangreco A.B., Shah A.H. Influence of anethole treatment on the tumour induced by Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells in paw of Swiss albino mice. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 1995;4(4):307–318. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources