The Clinical Value of the Combined Detection of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII), Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), and Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 39845022
- PMCID: PMC11752871
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S496703
The Clinical Value of the Combined Detection of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII), Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), and Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Objective: Gastric cancer (GC) is a common malignant tumor of the digestive tract. Accumulating studies suggest that inflammation is linked with the pathogenesis of GC. The study delves into novel hematological inflammatory markers, such as systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI), and prognostic nutritional index (PNI), to explore their potential applications in early diagnosis of GC.
Methods: From October 2020 and August 2024, 1339 GC patients admitted to our hospital were enrolled in this study. The pre-treatment SII, SIRI, and PNI was calculated from peripheral blood samples. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were utilized to verify independent risk factors for patients, and constructed the nomograms. The correlation between hematological indicators and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage was assessed through Spearman's analysis.
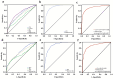
Results: Eligible patients and healthy controls were grouped by gender. The diagnostic ability of PNI was significantly superior to other indicators to diagnose male GC (area under the curve [AUC]=0.908, 95% CI: 0.892-0.925) and female GC (AUC=0.890, 95% CI: 0.865-0.914). Besides, the combination of hematological indicators is more effective in diagnosing GC patients, especially for male patients (AUC=0.916, 95% CI: 0.901-0.932, sensitivity: 84.98%, specificity: 84.29%). The C-statistic of Nomogram model was 0.917 for males and 0.875 for females. In both male and female cohorts, CEA, SII, and SIRI were positively correlated with TNM stage, while PNI was negatively correlated. The AUC of CEA, SII, SIRI, and PNI combined for the diagnosis in the early stage of male GC patients was 0.897 (95% CI: 0.875-0.918, sensitivity: 86.57%, specificity: 80.30%) is higher than that of in the advanced stage (AUC: 0.745, 95% CI: 0.710-0.780, sensitivity: 56.53%, specificity: 82.86%).
Conclusion: The combined CEA, SII, PNI, and SIRI could be used as screening biomarkers in diagnosing GC, especially in the early stage of male GC patients.
Keywords: PNI; SII; SIRI; early diagnosis; gastric cancer; prognostic nutritional index; systemic immune-inflammation index; systemic inflammation response index.
© 2025 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest of declare.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

