A systematic review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning approaches in Mexico: challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 39845096
- PMCID: PMC11753225
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2024.1479855
A systematic review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning approaches in Mexico: challenges and opportunities
Abstract
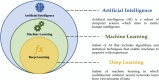
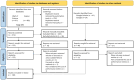
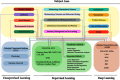
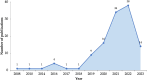
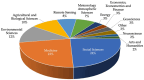
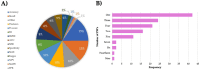
This systematic review provides a state-of-art of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models such as Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) development and its applications in Mexico in diverse fields. These models are recognized as powerful tools in many fields due to their capability to carry out several tasks such as forecasting, image classification, recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, etc. This review article aimed to provide comprehensive information on the Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms applied in Mexico. A total of 120 original research papers were included and details such as trends in publication, spatial location, institutions, publishing issues, subject areas, algorithms applied, and performance metrics were discussed. Furthermore, future directions and opportunities are presented. A total of 15 subject areas were identified, where Social Sciences and Medicine were the main application areas. It observed that Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) models were preferred, probably due to their capability to learn and model non-linear and complex relationships in addition to other popular models such as Random Forest (RF) and Support Vector Machines (SVM). It identified that the selection and application of the algorithms rely on the study objective and the data patterns. Regarding the performance metrics applied, accuracy and recall were the most employed. This paper could assist the readers in understanding the several Machine Learning and Deep Learning techniques used and their subject area of application in the Artificial Intelligence field in the country. Moreover, the study could provide significant knowledge in the development and implementation of a national AI strategy, according to country needs.
Keywords: Deep Learning; Machine Learning; Mexico; artificial intelligence; data science; state-of-the-art.
Copyright © 2025 Uc Castillo, Marín Celestino, Martínez Cruz, Tuxpan Vargas, Ramos Leal and Morán Ramírez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Crop yield prediction in agriculture: A comprehensive review of machine learning and deep learning approaches, with insights for future research and sustainability.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 29;10(24):e40836. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40836. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39720079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in Nutrition: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 6;16(7):1073. doi: 10.3390/nu16071073. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38613106 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Machine Learning Techniques in Soft Tissue Biomechanics and Biomaterials.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024 Oct;15(5):522-549. doi: 10.1007/s13239-024-00737-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024. PMID: 38956008 Review.
-
Applications of Artificial Intelligence to Obesity Research: Scoping Review of Methodologies.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Dec 7;24(12):e40589. doi: 10.2196/40589. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36476515 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in clinical care amidst COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:2833-2850. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 May 7. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abiodun O. I., Jantan A., Omolara A. E., Dada K. V., Umar A. M., Linus O. U., et al. . (2019). Comprehensive review of artificial neural network applications to pattern recognition. IEEE Access 7, 158820–158846. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2945545 - DOI
-
- Ahmed S., Alshater M. M., El Ammari A., Hammami H. (2022). Artificial intelligence and machine learning in finance: a bibliometric review. Res. Int. Bus. Finance 61:101646. doi: 10.1016/j.ribaf.2022.101646 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

