A management of patients achieving clinical complete response after neoadjuvant therapy and perspectives: on locally advanced rectal cancer
- PMID: 39845322
- PMCID: PMC11750660
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1450994
A management of patients achieving clinical complete response after neoadjuvant therapy and perspectives: on locally advanced rectal cancer
Abstract
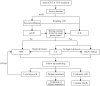
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) followed by total mesorectal excision (TME) and selective use of adjuvant chemotherapy is currently considered the standard of care for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). Despite this, the concept of organ preservation is gradually challenging this approach. The management of complete clinical remission (cCR) lacks international consensus, leading scholars to develop their own perspectives based on well-designed studies and long-term data from large multicenter cohorts. To ensure appropriate treatment, this review focuses on the choice of neoadjuvant therapy, criteria for defining cCR, and treatment strategies for patients who achieve cCR after neoadjuvant therapy. By providing guidance on the accurate management of LARC patients after cCR, this review aims to prevent over- or under-treatment.
Keywords: clinical complete response; locally advanced rectal cancer; neoadjuvant treatment; organ preservation; watch and wait policy.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Peng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fokas E, Liersch T, Fietkau R, Hohenberger W, Beissbarth T, Hess C, et al. . Tumor regression grading after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal carcinoma revisited: updated results of the CAO/ARO/AIO-94 trial. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:1554–62. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.54.3769 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

