Germline predisposition in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 39845416
- PMCID: PMC11750583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111620
Germline predisposition in multiple myeloma
Abstract
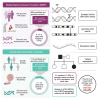
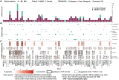
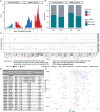
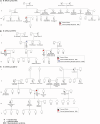
We present a study of rare germline predisposition variants in 954 unrelated individuals with multiple myeloma (MM) and 82 MM families. Using a candidate gene approach, we identified such variants across all age groups in 9.1% of sporadic and 18% of familial cases. Implicated genes included genes suggested in other MM risk studies as potential risk genes (DIS3, EP300, KDM1A, and USP45); genes involved in predisposition to other cancers (ATM, BRCA1/2, CHEK2, PMS2, POT1, PRF1, and TP53); and BRIP1, EP300, and FANCM in individuals of African ancestry. Variants were characterized using loss of heterozygosity (LOH), biallelic events, and gene expression analyses, revealing 31 variants in 3.25% of sporadic cases for which pathogenicity was supported by multiple lines of evidence. Our results suggest that the disruption of DNA damage repair pathways may play a role in MM susceptibility. These results will inform improved surveillance in high-risk groups and potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Cancer; Genetics; Molecular biology.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Landgren O., Kyle R.A., Pfeiffer R.M., Katzmann J.A., Caporaso N.E., Hayes R.B., Dispenzieri A., Kumar S., Clark R.J., Baris D., et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) consistently precedes multiple myeloma: a prospective study. Blood. 2009;113:5412–5417. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-194241. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

