Validation framework for in vivo digital measures
- PMID: 39845695
- PMCID: PMC11751004
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2024.1484895
Validation framework for in vivo digital measures
Abstract
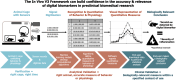
The adoption of in vivo digital measures in pharmaceutical research and development (R&D) presents an opportunity to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of discovering and developing new therapeutics. For clinical measures, the Digital Medicine Society's (DiMe) V3 Framework is a comprehensive validation framework that encompasses verification, analytical validation, and clinical validation. This manuscript describes collaborative efforts to adapt this framework to ensure the reliability and relevance of digital measures for a preclinical context. Verification ensures that digital technologies accurately capture and store raw data. Analytical validation assesses the precision and accuracy of algorithms that transform raw data into meaningful biological metrics. Clinical validation confirms that these digital measures accurately reflect the biological or functional states in animal models relevant to their context of use. By widely adopting this structured approach, stakeholders-including researchers, technology developers, and regulators-can enhance the reliability and applicability of digital measures in preclinical research, ultimately supporting more robust and translatable drug discovery and development processes.
Keywords: 3Rs (replace reduce refine); digital biomarkers; drug discovery and development; preclinical; rodents; translation; validation; verification.
Copyright © 2025 Baran, Bolin, Gaburro, van Gaalen, LaFollette, Liu, Maguire, Noldus, Bratcher-Petersen and Berridge.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SWB was employed by VeriSIM Life. Author SEB was employed by AbbVie Inc. Author SG was employed by Tecniplast SpA. Author MvG was employed by Evotec. Author ML was employed by The 3Rs Collaborative. Author C-NL was employed by Pfizer. Author SM was employed by GSK. Author LN was employed by Noldus Information Technology BV. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baran S. W., Bratcher N., Dennis J., Gaburro S., Karlsson E. M., Maguire S., et al. (2022). Emerging role of translational digital biomarkers within home cage monitoring technologies in preclinical drug discovery and development. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 15, 758274. 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.758274 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

