Anti-Scar Effects of Micropatterned Hydrogel after Glaucoma Drainage Device Implantation
- PMID: 39845708
- PMCID: PMC11751202
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0561
Anti-Scar Effects of Micropatterned Hydrogel after Glaucoma Drainage Device Implantation
Abstract
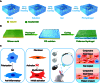
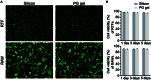
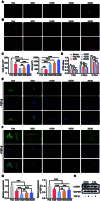
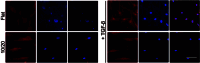
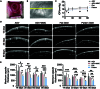
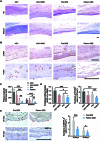
Excessive fibrosis is the primary factor for the failure of glaucoma drainage device (GDD) implantation. Thus, strategies to suppress scar formation in GDD implantation are crucial. Although it is known that in implanted medical devices, microscale modification of the implant surface can modulate cell behavior and reduce the incidence of fibrosis, in the field of ophthalmic implants, especially the modification and effects of hydrogel micropatterns have rarely been reported. Here, we designed the patterned gelatin/acrylamide double network hydrogel and developed an innovative GDD with micropattern to suppress inflammatory and fibroblast activation after GDD implantation. Pattern topography suppressed F-actin expression and mitigated actin-dependent nuclear migration of myocardin-related transcription factor A (MRTF-A) during the proliferative phase after GDD implantation. Ultimately, the expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), a key fibrosis-related gene product, was suppressed. Moreover, the modified GDD effectively controlled intraocular pressure (IOP), mitigated fibrous formation, and remodeled extracellular matrix (ECM) collagen distribution in vivo. Therefore, the novel GDD with surface patterning interventions provides a promising strategy to inhibit scar formation after GDD implantation and raise the efficacy of GDD implantation.
Copyright © 2025 Yiling Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Corneal graft survival and intraocular pressure control after penetrating keratoplasty and glaucoma drainage device implantation.Ophthalmology. 2001 Nov;108(11):1978-85. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(01)00803-x. Ophthalmology. 2001. PMID: 11713065
-
Grooved Glaucoma Drainage Devices That Continuously Deliver Cyclosporine A Decrease Postsurgical Scar Formation in Rabbit Eyes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Mar 1;58(3):1692-1701. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-21065. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28319643
-
A Comparison of Sequential Glaucoma Drainage Device Implantation Versus Cyclophotocoagulation Following Failure of a Primary Drainage Device.J Glaucoma. 2017 Apr;26(4):311-314. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000370. J Glaucoma. 2017. PMID: 26859357 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of glaucoma drainage device].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jun;45(6):567-73. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19957681 Review. Chinese.
-
Comparison of pars plana with anterior chamber glaucoma drainage device implantation for glaucoma: a meta-analysis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Aug 29;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0896-x. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30157805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Souza C, Tran DH, Loman J, Law SK, Coleman AL, Caprioli J. Long-term outcomes of Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation in refractory glaucomas. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;144(6):893–900. - PubMed
-
- Lama PJ, Fechtner RD. Antifibrotics and wound healing in glaucoma surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48(3):314–346. - PubMed
-
- Dai Z, Yu X, Sun J, Sun X. Grooved glaucoma drainage devices that continuously deliver cyclosporine a decrease postsurgical scar formation in rabbit eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(3):1692–1701. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

