The efficacy and safety of qiwei baizhu san in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39845797
- PMCID: PMC11752898
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1501990
The efficacy and safety of qiwei baizhu san in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, mostly resulting from impaired insulin production and diminished glucose metabolism regulation. Qiwei Baizhu San (QWBZS) is a classic formula used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of T2DM. A comprehensive analysis of the efficacy and safety of QWBZS in the treatment of T2DM is essential.
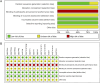
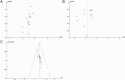
Methods: This study's protocol was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024576129). As of August 2024, we searched eight databases to screen and include randomized controlled trials of QWBZS for T2DM. Heterogeneity sources were examined via subgroup analyses, the robustness of the results was determined by sensitivity analyses, publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots and Egger's test, evidence quality was appraised with GRADEpro, and possible mechanisms of QWBZS for T2DM were categorized and summarized.
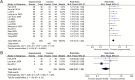
Results: This analysis encompassed 14 qualifying trials with a total of 1,169 subjects. The analytical results suggested that QWBZS, when combined with conventional treatment, was more effective than conventional treatment alone in improving FBG, 2hPG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C. When QWBZS was used alone, it was more effective than conventional therapy in FBG, 2hPG, and HbA1c. And QWBZS could improve the overall effectiveness of clinical treatment in T2DM patients. The impact of QWBZS therapy alone on HOMA-IR and lipid metabolism remained unclear due to the limited number of trials included. Analysis of adverse events suggested that QWBZS was relatively safe.
Conclusion: This study suggested that QWBZS, when combined with conventional treatment, was more effective in improving glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism compared to conventional treatment alone in individuals with T2DM. QWBZS alone also contributed to the regulation of blood glucose levels. Meanwhile, QWBZS could improve the overall effective rate of clinical treatment with a relatively high safety profile. Nevertheless, owing to the inferior quality and significant heterogeneity of the existing evidence, additional high-quality studies are requisite to furnish more dependable evidence for the future clinical application of QWBZS.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=576129, identifier [CRD42024576129].
Keywords: meta-analysis; qiwei baizhu san; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Liu, Zhang, Ouyang, Fu and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:918681. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918681. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003504 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine as an add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with carotid atherosclerosis: An updated meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1091718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1091718. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033624 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of Coptis chinensis Franch.-containing traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunct therapy to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 8;13:956313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.956313. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160405 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extract combined with ACEI/ARB on diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 41 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1408546. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1408546. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39830333 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 26;14:1316269. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1316269. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38344688 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

