Interaction between Th17 and central nervous system in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 39845807
- PMCID: PMC11751430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100928
Interaction between Th17 and central nervous system in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
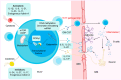
Image 1.
Keywords: CNS; Cytokine network; Immune therapy; Multiple sclerosis; Th17.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17 cells in central nervous system autoimmunity.Exp Neurol. 2014 Dec;262 Pt A:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24681001 Review.
-
Recognition of viral and self-antigens by TH1 and TH1/TH17 central memory cells in patients with multiple sclerosis reveals distinct roles in immune surveillance and relapses.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Sep;140(3):797-808. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.11.045. Epub 2017 Feb 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28237728
-
Magnolol as STAT3 inhibitor for treating multiple sclerosis by restricting Th17 cells.Phytomedicine. 2023 Aug;117:154917. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154917. Epub 2023 Jun 3. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37301184
-
Metabolic Control of Th17 Cell Generation and CNS Inflammation.J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2014;Suppl 12:S12-004. doi: 10.4172/2155-9562.S12-004. J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 25705564 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Parkinson's Disease, Alzheimer's Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5177. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115177. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acharya S., Timilshina M., Jiang L., Neupane S., Choi D.-Y., Park S.W., Chang J.-H. Amelioration of Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and DSS induced colitis by NTG-A-009 through the inhibition of Th1 and Th17 cells differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2018;8(1):7799. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26088-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S.F., Nadeem A., Ansari M.A., Bakheet S.A., Shahid M., Al-Mazroua H.A.…Attia S.M. CC chemokine receptor 5 antagonist alleviates inflammation by regulating IFN-γ/IL-10 and STAT4/Smad 3 signaling in a mouse model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cell. Immunol. 2022;379 doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104580. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S.F., Ansari M.A., Nadeem A., Bakheet S.A., Alasmari A.F., Shahid M.…Attia S.M. MAP kinase inhibitor PD98059 regulates Th1, Th9, Th17, and natural T regulatory cells in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023;959 doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176086. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S.F., Ansari M.A., Nadeem A., Bakheet S.A., Al-Mazroua H.A., Alomar H.A., Attia S.M. S3I-201, a selective stat3 inhibitor, ameliorates clinical symptoms in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through the regulation of multiple intracellular signalling in Th1, Th17, and treg cells. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023;73 doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.104658. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Kharashi L.A., Al-Harbi N.O., Ahmad S.F., Attia S.M., Algahtani M.M., Ibrahim K.E.…Nadeem A. Auranofin modulates thioredoxin reductase/nrf2 signaling in peripheral immune cells and the CNS in a mouse model of relapsing-remitting EAE. Biomedicines. 2023;11(9) doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092502. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

