A positive relationship between weight-adjusted waist index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a study on US adolescents
- PMID: 39845834
- PMCID: PMC11753237
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1424667
A positive relationship between weight-adjusted waist index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a study on US adolescents
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver condition in children, underscoring the urgent need for non-invasive markers for early detection in this population.
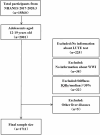
Methods: We utilized survey data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2017-2020 regarding liver ultrasound transient elastography (LUTE) for the diagnosis of NAFLD (dependent variable), and used multiple logistic regression models to explore the association between weight-adjusted waist circumference index (WWI) and the prevalence of NAFLD in US adolescents. Smoothing curves and threshold effect analyses were used to assess the non-linear association between the independent variables and the dependent variable. Subgroup analysis was conducted to pinpoint particularly susceptible subgroups within our study cohort of 1,711 participants.
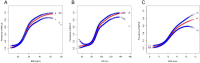
Results: Our findings indicated a positive correlation between WWI and NAFLD scores. Adjusting for all covariates revealed a significant association between increased WWI and the presence of NAFLD, with an odds ratio of 3.37 (95% CI: 2.74, 4.15). This association proved stronger than those observed with waist circumference, body mass index, and NAFLD. Stratifying WWI into quartiles showed a clear and strong positive correlation (P for trend < 0.0001). The results of smoothing curves and threshold effect analysis showed a non-linear relationship between WWI and NAFLD (LLR < 0.001). Notably, for WWI values below 10.65, a significant correlation was observed (OR = 5.25, 95% CI: 3.77,7.31). Additionally, our subgroup analysis revealed that WWI and NAFLD were associated more positively among male participants aged 16 years and older.
Conclusion: WWI is positively correlated with NAFLD in American adolescents and offers a straightforward and cost-effective method for identifying hepatic steatosis. The findings highlight the importance of focusing on individuals with a WWI below 10.65, where the risk of NAFLD increases. Priority should be given to the male adolescent population aged 16 and above.
Keywords: BMI; adolescents; liver steatosis; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; waist circumference; weight-adjusted waist index.
Copyright © 2025 Cui, Huang, Kang, Han, Sun, Han and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of weight-adjusted-waist index with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Aug 3;28(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01205-4. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37537679 Free PMC article.
-
Association between weight-adjusted waist index and hepatic steatosis and fibrosis: Analyses of the NHANES 2017 to 2020.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 6;104(23):e42708. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042708. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40489808 Free PMC article.
-
Association between weight-adjusted waist index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Feb 18;24(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01554-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 38369482 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Depression in NAFLD: the modulating roles of sex and BMI.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 20;24(1):838. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06308-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39567895 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and depressive symptoms: A nationally representative cross-sectional study from NHANES 2005 to 2018.J Affect Disord. 2024 Apr 1;350:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.01.104. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38220117 Review.
Cited by
-
Application value of weight-adjusted waist circumference index and cardiometabolic index in hypertensive patients with albuminuria: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2020.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2506813. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2506813. Epub 2025 May 28. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40437733 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

