Case report: Looking for relationship between type 1 diabetes and chronic recurrent osteomyelitis: short literature review and case presentation
- PMID: 39845887
- PMCID: PMC11750682
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1505382
Case report: Looking for relationship between type 1 diabetes and chronic recurrent osteomyelitis: short literature review and case presentation
Abstract
Background: Childhood autoimmune disorders involve the immune system attacking its own tissues, leading to varied symptoms, while autoinflammatory disorders result from innate immune system dysregulation, both requiring extensive diagnosis and multidisciplinary management due to their complexity.
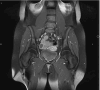
Case presentation: We present a unique clinical case of a teenager with a combination of autoimmune and autoinflammatory disorders. The initial manifestation of hip pain, coupled with progressive symptoms over several years and findings in multiple magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, culminated in the diagnosis of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO). Subsequently, the patient was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D), celiac disease, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.The therapeutic course proved challenging, marked by unsuccessful attempts with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and biphosphonates. However, a stable clinical status was ultimately achieved upon the introduction of methotrexate, concomitant with insulin therapy for diabetes and the implementation of a gluten-free diet for celiac disease.
Conclusions: Our case showed that the combination of autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, brought not only a challenging diagnostic process, but also complicated treatment.
Keywords: autoimmunity; autoinflammation; celiac disease; chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Snipaitiene, Radzeviciute, Aleknaviciene, Dobrovolskiene and Stankute.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pohl D, Bendeler S. Systematic inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 112 (3rd series). Pediatric Neurology Part II. Netherlands: Elsevier; (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

