Multiscale Three-Dimensional Evaluation and Analysis of Murine Lung Vasculature From Macro- to Micro-Structural Level
- PMID: 39845890
- PMCID: PMC11751252
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.70038
Multiscale Three-Dimensional Evaluation and Analysis of Murine Lung Vasculature From Macro- to Micro-Structural Level
Abstract
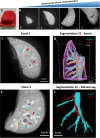
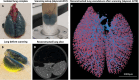
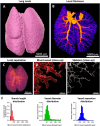
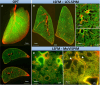
The pulmonary vasculature plays a pivotal role in the development and progress of chronic lung diseases. Due to limitations of conventional two-dimensional histological methods, the complexity and the detailed anatomy of the lung blood circulation might be overlooked. In this study, we demonstrate the practical use of optical serial block face imaging (SBFI), ex vivo microcomputed tomography (micro-CT), and nondestructive optical tomography for visualization and quantification of the pulmonary circulation's 3D architecture from macro- to micro-structural levels in murine lung samples. We demonstrate that SBFI can provide rapid, cost-effective, and label-free visualization of mouse lung macrostructures and large pulmonary vessels. Micro-CT offers high-resolution imaging and captures microvascular and (pre)capillary structures, with microstructural quantification. Optical microscopy techniques such as optical projection tomography (OPT) and light sheet fluorescence microscopy, allows noninvasive, mesoscopic imaging of optically cleared mouse lungs, still enabling 3D microscopic reconstruction down to the precapillary level. By integrating SBFI, micro-CT, and nondestructive optical microscopy, we provide a framework for detailed and 3D understanding of the pulmonary circulation, with emphasis on vascular pruning and rarefaction. Our study showcases the applicability and complementarity of these techniques for organ-level vascular imaging, offering researchers flexibility in selecting the optimal approach based on their specific requirements. In conclusion, we propose 3D-directed approaches for a detailed whole-organ view on the pulmonary vasculature in health and disease, to advance our current knowledge of diseases affecting the pulmonary vasculature.
Keywords: 3D visualization and evaluation; microcomputed tomography; optical imaging; pulmonary vasculature; serial block face imaging.
© 2025 The Authors. Pulmonary Circulation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Image acquisition and data collection at the Kratoscope were performed at Kaer Labs company, Nantes, France. P.D.V. and P.D. are employees of the company Kaer Labs.
Figures
References
-
- Huertas A., Guignabert C., Barberà J. A., et al., “Pulmonary Vascular Endothelium: The Orchestra Conductor in Respiratory Diseases: Highlights From Basic Research to Therapy,” European Respiratory Journal 51, no. 4 (2018): 1700745. - PubMed
-
- Blanco I., Piccari L., and Barberà J. A., “Pulmonary Vasculature in COPD: The Silent Component,” Respirology 21, no. 6 (2016): 984–994. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

