Impact of glioma metabolism-related gene ALPK1 on tumor immune heterogeneity and the regulation of the TGF-β pathway
- PMID: 39845963
- PMCID: PMC11753219
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1512491
Impact of glioma metabolism-related gene ALPK1 on tumor immune heterogeneity and the regulation of the TGF-β pathway
Abstract
Background: Recent years have seen persistently poor prognoses for glioma patients. Therefore, exploring the molecular subtyping of gliomas, identifying novel prognostic biomarkers, and understanding the characteristics of their immune microenvironments are crucial for improving treatment strategies and patient outcomes.
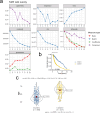
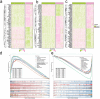
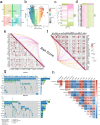
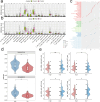
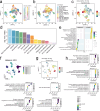
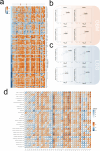
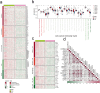
Methods: We integrated glioma datasets from multiple sources, employing Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) to cluster samples and filter for differentially expressed metabolic genes. Additionally, we utilized Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) to identify key genes. A predictive model was developed utilizing the optimal consistency index derived from a combination of 101 machine learning techniques, and its effectiveness was confirmed through multiple datasets employing different methodologies. In-depth analyses were conducted on immune cell infiltration and tumor microenvironmental aspects. Single-cell sequencing data were employed for clustering and differential expression analysis of genes associated with glioma. Finally, the immune relevance of the model gene ALPK1 in the context of pan-cancer was explored, including its relationship with immune checkpoints.
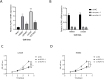
Results: The application of NMF, coupled with differential analysis of metabolic-related genes, led to the identification of two clusters exhibiting significant differences in survival, age, and metabolic gene expression among patients. Core genes were identified through WGCNA, and a total of 101 machine learning models were constructed, with LASSO+GBM selected as the optimal model, demonstrating robust validation performance. Comprehensive analyses revealed that high-risk groups exhibited greater expression of specific genes, with ALPK1 showing significant correlations with immune regulation.
Conclusion: This research employed a multi-dataset strategy and various methods to clarify the differences in metabolic traits and immune conditions in glioma patients, while creating an innovative prognostic risk evaluation framework. These results offer fresh perspectives on the intricate biological processes that define gliomas.
Keywords: ALPK1; glioma; immune microenvironment; metabolic genes; prognostic biomarkers.
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Qin and Deng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of NOD-like receptor-based molecular heterogeneity in glioma and its association with immune micro-environment and metabolism reprogramming.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 15;15:1498583. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1498583. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39882240 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic model of low-grade glioma based on m6A-associated immune genes and functional study of FBXO4 in the tumor microenvironment.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 21;13:e19194. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19194. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40130175 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics exploration of SPHKAP's role in IDH-mutant glioma involving energy metabolism, prognosis, and immune modulation.J Neuroimmunol. 2025 May 15;402:578570. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2025.578570. Epub 2025 Mar 4. J Neuroimmunol. 2025. PMID: 40058165
-
Prognostic prediction and immune checkpoint profiling in glioma patients through neddylation-associated features.Gene. 2024 Dec 20;930:148835. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148835. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Gene. 2024. PMID: 39127414
-
Annexin A's Life in Pan-Cancer: Especially in Glioma Immune Cells.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 Feb 26;27(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s12017-024-08827-9. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40011350 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell sequencing combined with machine learning to identify glioma biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 24;15:1629102. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1629102. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40777122 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

