DNA2 knockout aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing postsynaptic Homer1a
- PMID: 39846189
- PMCID: PMC11890998
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.269
DNA2 knockout aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing postsynaptic Homer1a
Abstract
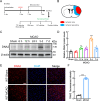
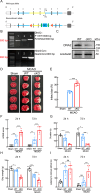
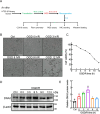
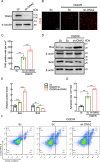
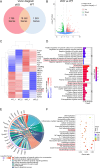
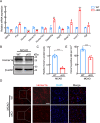
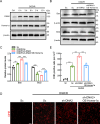
DNA2, a multifunctional enzyme with structure-specific nuclease, 5 '-to-3 ' helicase, and DNA-dependent ATPase activities, plays a pivotal role in the cellular response to DNA damage. However, its involvement in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains to be elucidated. This study investigated the involvement of DNA2 in cerebral I/R injury using conditional knockout (cKO) mice ( Nestin-Cre) subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), an established model of cerebral I/R. Results demonstrated a gradual up-regulation of DNA2 expression, peaking at 72 h post-MCAO. Notably, DNA2 cKO mice exhibited more pronounced brain injury, neurological deficits, and neuronal apoptosis within the penumbra following MCAO. Additionally, DNA2 expression was elevated in an oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) cell culture model, and DNA2 knockdown (KD) exacerbated neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress. Transcriptome analysis of ischemic penumbra tissues via RNA sequencing revealed significant down-regulation of Homer1 in DNA2 cKO mice. Furthermore, in vitro experiments demonstrated that overexpression of Homer1a ameliorated DNA2 KD-induced neuronal apoptosis. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that DNA2 deficiency exacerbates cerebral I/R injury through the down-regulation of Homer1a, highlighting a novel regulatory axis in ischemic neuroprotection.
DNA2是一种多功能酶,在冈崎片段加工、端粒维护、DNA双链断裂修复以及DNA复制叉处理等过程中发挥关键作用,对基因组稳定性至关重要。然而,DNA2在脑缺血/再灌注(Ischemia/reperfusion,I/R)损伤中的作用尚未明确。该研究利用 DNA2条件性敲除(Conditional knockout,cKO)小鼠,通过建立大脑中动脉闭塞(Middle cerebral artery occlusion,MCAO)模型探讨其功能。结果显示,MCAO后DNA2表达逐渐上调,并在72小时达到峰值。值得注意的是,cKO小鼠在MCAO后表现出显著的神经功能缺损和半暗带神经元凋亡。此外,在氧糖剥夺/复氧(Oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation,OGD/R)细胞模型中, DNA2敲低(Knockdown,KD)加剧了神经元凋亡和氧化应激反应。为进一步探究 DNA2在脑I/R损伤中的机制,我们对缺血半暗带组织进行了全转录组测序(Transcriptome sequencing,RNA-seq),结果发现,cKO小鼠的 Homer1表达显著下调。此外, Homer1a过表达能够改善 DNA2 KD引起的神经元凋亡。综上所述,该研究表明, DNA2敲除通过下调 Homer1a表达加剧脑I/R损伤。.
Keywords: Cerebral I/R; DNA2; Homer1a; Neuronal apoptosis; OGD/R.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Piezo1 Modulates Neuronal Autophagy and Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through the AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2024 Nov 25;50(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04291-w. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39585469
-
LncRNA MALAT1 improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and cognitive dysfunction by regulating miR-142-3p/SIRT1 axis.Int J Neurosci. 2023 Jul;133(7):740-753. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2021.1972999. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Int J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 34461809
-
TRPC1 Deficiency Exacerbates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Neurological Injury by Potentiating Nox4-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Generation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(4):1723-1738. doi: 10.1159/000495676. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30504729
-
Expression and regulation of miR-449a and AREG in cerebral ischemic injury.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Jun;34(3):821-832. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-0393-9. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30773606
-
Downregulation of Nogo-B ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through regulating microglia polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jul;167:105553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105553. Epub 2023 May 23. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 37230196 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
