A method for facile production of variable lymphocyte receptors using SHuffle Escherichia coli
- PMID: 39846486
- PMCID: PMC12171313
- DOI: 10.1002/btpr.3530
A method for facile production of variable lymphocyte receptors using SHuffle Escherichia coli
Abstract
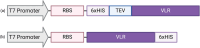
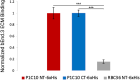
Variable lymphocyte receptors (VLRs) are the antigen receptors of jawless vertebrates such as lamprey. VLRs are of growing biotechnological interest for their ability to bind certain antigenic targets with higher affinity than traditional immunoglobulins. However, VLRs are disulfide-bonded proteins that are often challenging to produce requiring genetic modifications, fusion partners, non-scalable host cell lines or inclusion body formation and refolding. As a potential VLR expression platform option, the SHuffle Escherichia coli strain has been genetically altered to allow cytoplasmic disulfide bond formation by mutations to thioredoxin reductase (trxB) and glutathione reductase (gor) to create an oxidative cytoplasm. Furthermore, the SHuffle strain expresses disulfide bond isomerase DsbC in the cytoplasm to promote correct disulfide bond pairing. Here, we demonstrate that the SHuffle strain can produce high yield VLRs with titers ranging from 2 to 32 mg of VLR per liter of SHuffle culture. Three VLRs (P1C10, RBC36, VLRA.R2.1) were expressed in SHuffle E. coli and the products were compared directly to those generated using the Rosetta E. coli strain. All VLRs were validated for correct sequence, purity, and activity. For all VLRs, SHuffle E. coli produced 2-9 times more soluble VLRs than Rosetta E. coli. Furthermore, the soluble protein fraction was 2-6 times greater in SHuffle E. coli than Rosetta E. coli for all VLRs. Overall, these results suggest that the E. coli SHuffle strain is a convenient and effective expression system for producing large amounts of VLRs.
Keywords: SHuffle E. Coli; bacterial protein expression; disulfide bonds; variable lymphocyte receptors.
© 2025 The Author(s). Biotechnology Progress published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
Eric V. Shusta has filed a US patent application regarding uses for the P1C10 VLR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient production of functional proaerolysin in E. coli.Protein Expr Purif. 2025 Oct;234:106754. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2025.106754. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Protein Expr Purif. 2025. PMID: 40480299
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Herrin BR, Cooper MD. Alternative adaptive immunity in jawless vertebrates. J Immunol. 2010;185(3):1367‐1374. - PubMed
-
- Pancer Z, Amemiya CT, Ehrhardt GRA, Ceitlin J, Larry Gartland G, Cooper MD. Somatic diversification of variable lymphocyte receptors in the agnathan sea lamprey. Nature. 2004;430(6996):174‐180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

