NT-proBNP for Heart Failure Screening in Primary Care in an Eastern European Country: What We Know and Proposed Steps
- PMID: 39846532
- PMCID: PMC11755574
- DOI: 10.3390/epidemiologia6010002
NT-proBNP for Heart Failure Screening in Primary Care in an Eastern European Country: What We Know and Proposed Steps
Abstract
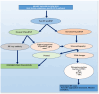
Epidemiological studies indicate that heart failure (HF) prevalence and associated mortality are significantly higher among Eastern European countries as compared to their Western European counterparts. The significant financial burden on the healthcare system matches these sobering data. Thus, efficient programs for patients with HF have been called for. N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) represents a widely used, cost-effective, and readily available test that can be used to evaluate HF risk. However, it should not be used as a universal assessment, given the existing variability in proposed cut-off scores for various subgroups of patients. Thus, the clinical context needs to always be considered, and alternative diagnoses need to be ruled out. Based upon evidence from the literature for the above assumptions, the advantages and limitations of using NT-proBNP in primary care settings, along with other HF diagnostic modalities, are discussed in this paper. Also, this paper argues that an effective primary care network, in collaboration with specialist providers, may avoid a delay in HF diagnoses, may help provide on-time treatments, and may ultimately cut unnecessary healthcare expenditures associated with HF hospitalizations. Therefore, the present paper proposes an algorithm for diagnosing HF in primary care settings and discusses specific knowledge and skills that family physicians should be well equipped with in order to successfully respond to the needs of their patients with HF.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; heart failure; primary care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and N-Terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) as Diagnostic Tests in Adults With Suspected Heart Failure: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021 May 6;21(2):1-125. eCollection 2021. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021. PMID: 34055110 Free PMC article.
-
Ruling out heart failure in primary-care: the cost-benefit of pre-screening using NT-proBNP and QRS width.Int J Cardiol. 2008 Nov 28;130(3):426-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.08.131. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Int J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18178273
-
Cost-effectiveness of NT-proBNP-supported screening of chronic heart failure in patients with or without type 2 diabetes in Austria and Switzerland.J Med Econ. 2023 Jan-Dec;26(1):1287-1300. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2264722. Epub 2023 Oct 18. J Med Econ. 2023. PMID: 37781889
-
[Diagnostic value of the currently used criteria and brain natriuretic peptide for diagnosing congestive heart failure in children with congenital heart disease].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Oct;44(10):728-32. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17229370 Chinese.
-
Natriuretic peptide family as diagnostic/prognostic biomarker and treatment modality in management of adult and geriatric patients with heart failure: remaining issues and challenges.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2018 Aug;15(8):540-546. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2018.08.008. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30344534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Quality of Life of Patients in Romania with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction by Analyzing H2FPEF Scores.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;13(8):909. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080909. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281858 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;16(3):305. doi: 10.3390/genes16030305. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chioncel O., Čelutkienė J., Bělohlávek J., Kamzola G., Lainscak M., Merkely B., Miličić D., Nessler J., Ristić A.D., Sawiełajc L., et al. Heart Failure Care in the Central and Eastern Europe and Baltic Region: Status, Barriers, and Routes to Improvement. ESC Heart Fail. 2024;11:1861–1874. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14687. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Societatea Romana de Cardiologie. Fundatia Romana a Inimii. Societatea Nationala de Medicina Familiei. C.O.P.A.C. Document Pozitie: Constientizarea Si Managementul Imbunatatit al Insuficientei Cardiace. Societatea Romana de Cardiologie; Bucharest, Romania: 2021.
-
- Chioncel O., Tatu-Chitoiu G., Christodorescu R., Coman I.M., Deleanu D., Vinereanu D., Macarie C., Crespo M., Laroche C., Fereirra T., et al. Characteristics of Patients with Heart Failure from Romania Enrolled in ESC-HF Long-Term (ESC-HF-LT) Registry. Romanian J. Cardiol. 2015;25
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous