Cardiotoxicity of Chemotherapy: A Multi-OMIC Perspective
- PMID: 39846541
- PMCID: PMC11755476
- DOI: 10.3390/jox15010009
Cardiotoxicity of Chemotherapy: A Multi-OMIC Perspective
Abstract
Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity is a critical issue in cardio-oncology, as cancer treatments often lead to severe cardiovascular complications. Approximately 10% of cancer patients succumb to cardiovascular problems, with lung cancer patients frequently experiencing arrhythmias, cardiac failure, tamponade, and cardiac metastasis. The cardiotoxic effects of anti-cancer treatments manifest at both cellular and tissue levels, causing deformation of cardiomyocytes, leading to contractility issues and fibrosis. Repeated irradiation and chemotherapy increase the risk of valvular, pericardial, or myocardial diseases. Multi-OMICs analyses reveal that targeting specific pathways as well as specific protein modifications, such as ubiquitination and phosphorylation, could offer potential therapeutic alternatives to current treatments, including Angiotensin converting enzymes (ACE) inhibitors and beta-blockers that mitigate symptoms but do not prevent cardiomyocyte death, highlighting the need for more effective therapies to manage cardiovascular defects in cancer survivors. This review explores the xenobiotic nature of chemotherapy agents and their impact on cardiovascular health, aiming to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets to mitigate cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: cancer; cardiotoxicity; cardiovascular diseases; chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




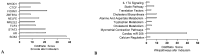




References
-
- Dos Santos V.M., Dos Santos L.A.M. Cardiac and lymphatic metastases from lung cancer. Arch. Iran. Med. 2018;21:82–83. - PubMed
-
- Mizutani H., Kume H., Kimura T., Ogawa M., Yoshida N., Yoshida M., Ito Y., Suzuki R., Yamaki K. Primary lung cancer (adenocarcinoma) associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi = J. Jpn. Respir. Soc. 1999;37:489–494. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

