DNA and RNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39846569
- PMCID: PMC11755448
- DOI: 10.3390/epigenomes9010002
DNA and RNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Narrative Review
Abstract
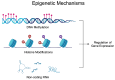
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a progressive autoimmune disease leading to structural and functional joint damage and, eventually, to physical disability. The pathogenesis of the disease is highly complex and involves interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) and immune cells, which stimulate the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors, leading to chronic inflammation. In recent years, studies have demonstrated the importance of epigenetics in RA. Specifically, epigenetic alterations have been suggested to serve as diagnostic and treatment biomarkers, while epigenetic mechanisms are thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. Epigenetic regulators coordinate gene expression, and in the case of inflammatory diseases, they regulate the expression of a broad range of inflammatory molecules. In this review, we discuss current evidence on the involvement of DNA and RNA methylation in RA.
Keywords: DNA methylation; RNA methylation; epigenetics; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

