Epigenetics in Skin Homeostasis and Ageing
- PMID: 39846570
- PMCID: PMC11755608
- DOI: 10.3390/epigenomes9010003
Epigenetics in Skin Homeostasis and Ageing
Abstract
The skin, the largest organ of the human body, plays numerous essential roles, including protection against environmental hazards and the regulation of body temperature. The processes of skin homeostasis and ageing are complex and influenced by many factors, with epigenetic mechanisms being particularly significant. Epigenetics refers to the regulation of gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. The dynamic nature of the skin, characterized by constant cellular turnover and responsiveness to environmental stimuli, requires precise gene activity control. This control is largely mediated by epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and regulation by non-coding RNAs. The present review endeavours to provide a comprehensive exploration and elucidation of the role of epigenetic mechanisms in regulating skin homeostasis and ageing. By integrating our current knowledge of epigenetic modifications with the latest advancements in dermatological research, we can gain a deeper comprehension of the complex regulatory networks that govern skin biology. Understanding these mechanisms also presents promising avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at improving skin health and mitigating age-related skin conditions.
Keywords: DNA methylation; ageing; epidermis; epigenetics; histone modification; homeostasis; non-coding RNAs; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
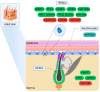
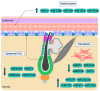
References
-
- Lotfollahi Z. The Anatomy, Physiology and Function of All Skin Layers and the Impact of Ageing on the Skin. Wound Pract. Res. 2024;32:6–10. doi: 10.33235/wpr.32.1.6-10. - DOI
-
- Abdo J.M., Sopko N.A., Milner S.M. The Applied Anatomy of Human Skin: A Model for Regeneration. Wound Med. 2020;28:100179. doi: 10.1016/j.wndm.2020.100179. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

