Newborn Screening by DNA-First: Systematic Evaluation of the Eligibility of Inherited Metabolic Disorders Based on Treatability
- PMID: 39846587
- PMCID: PMC11755635
- DOI: 10.3390/ijns11010001
Newborn Screening by DNA-First: Systematic Evaluation of the Eligibility of Inherited Metabolic Disorders Based on Treatability
Abstract
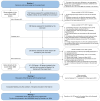
The biomarker-based Dutch Newborn Screening (NBS) panel (as of 2024) comprises 19 inherited metabolic disorders (IMDs). With the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) as a first-tier screen, NBS could expand to include IMDs that lack a reliable biochemical footprint in dried blood spots, while also reducing secondary findings. To be eligible for inclusion in NBS, an IMD needs to fulfill the Wilson and Jungner criteria, with treatability being one of the most important criteria. In this study, we aimed to identify IMDs eligible for DNA-first NBS when considering only treatability in the context of NBS as a prerequisite. First, three independent reviewers performed a systematic literature review of the 1459 genotypic IMDs and their causative gene(s), as described in the International Classification of Inherited Metabolic Disorders (dated 1 February 2021), applying 16 criteria to exclude non-treatable disorders. Eligible disorders were then discussed in three online meetings with a project group of clinical laboratory geneticists, medical laboratory specialists specialized in IMD, and pediatricians with expertise in IMDs. Based on treatability, we identified 100 genes, causing 95 IMDs, as eligible for NBS, including 42 causal genes for the IMDs in the current biomarker-based NBS. The other 58 genes are primarily associated with treatable defects in amino acid metabolism and fatty acid oxidation. Other IMDs were excluded, most often because of insufficient literature. As the evaluation of treatability was not straightforward, we recommend the development of standardized treatability scores for the inclusion of IMDs in NBS.
Keywords: Wilson and Jungner criteria; genetics-first; heel prick; inborn errors of metabolism; inherited metabolic disease; newborn screening; next-generation sequencing; treatability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- TNO . The Newborn Blood Spot Screening Monitor 2019. TNO; The Hague, The Netherlands: 2021. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu-Centrum voor Bevolkingsonderzoek.
-
- TNO . The Newborn Blood Spot Screening Monitor 2020. TNO; The Hague, The Netherlands: 2022. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu-Centrum voor Bevolkingsonderzoek.
-
- TNO . The Newborn Blood Spot Screening Monitor 2021. TNO; The Hague, The Netherlands: 2023. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu-Centrum voor Bevolkingsonderzoek.
-
- TNO . The Newborn Blood Spot Screening Monitor 2022. TNO; The Hague, The Netherlands: 2023. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu-Centrum voor Bevolkingsonderzoek.
-
- National Institute for Public Health and Environment. Pre- and Neonatal Screenings (PNS), Heel Prick Screening Test [1]. Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. 2024. [(accessed on 30 June 2024)]. Available online: https://www.pns.nl/en/prenatal-and-newborn-screening/heel-prick-screenin....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

