Advancing Newborn Screening in Washington State: A Novel Multiplexed LC-MS/MS Proteomic Assay for Wilson Disease and Inborn Errors of Immunity
- PMID: 39846592
- PMCID: PMC11755445
- DOI: 10.3390/ijns11010006
Advancing Newborn Screening in Washington State: A Novel Multiplexed LC-MS/MS Proteomic Assay for Wilson Disease and Inborn Errors of Immunity
Abstract
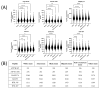
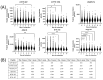
For many genetic disorders, there are no specific metabolic biomarkers nor analytical methods suitable for newborn population screening, even where highly effective preemptive treatments are available. The direct measurement of signature peptides as a surrogate marker for the protein in dried blood spots (DBSs) has been shown to successfully identify patients with Wilson Disease (WD) and three life-threatening inborn errors of immunity, X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS), and adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADAD). A novel proteomic-based multiplex assay to detect these four conditions from DBS using high-throughput LC-MS/MS was developed and validated. The clinical validation results showed that the assay can accurately identify patients of targeted disorders from controls. Additionally, 30,024 newborn DBS samples from the Washington State Department of Health Newborn Screening Laboratory have been screened from 2022 to 2024. One true presumptive positive case of WD was found along with three false positive cases. Five false positives for WAS were detected, but all of them were premature and/or low-birth-weight babies and four of them had insufficient DNA for confirmation. The pilot study demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of utilizing this multiplexed proteomic assay for newborn screening.
Keywords: Wilson Disease; Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome; X-linked agammaglobulinemia; adenosine deaminase deficiency; mass spectrometry; newborn screening; peptide; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Sihoun Hahn, MD, PhD, is a member of the Seattle Children’s Hospital workforce and is serving as a Chief Medical Officer of Key Proteo, Inc. He is an inventor of intellectual property that has been licensed to Key Proteo, Inc. Dr. Hahn is the founder of Key Proteo, Inc. and has ownership equity interests in the company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid Multiplexed Proteomic Screening for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders From Dried Blood Spots.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 4;9:2756. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02756. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30564228 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed Proteomic Analysis for Diagnosis and Screening of Five Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders From Dried Blood Spots.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 1;11:464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00464. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32296420 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptic peptide screening for primary immunodeficiency disease by LC/MS-MS.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012 Aug;6(7-8):394-402. doi: 10.1002/prca.201100096. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012. PMID: 22927353 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Newborn Screening Laboratories.Int J Neonatal Screen. 2022 Nov 28;8(4):62. doi: 10.3390/ijns8040062. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2022. PMID: 36547379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Newborn screening.Pathology. 2008 Feb;40(2):104-15. doi: 10.1080/00313020701813743. Pathology. 2008. PMID: 18203033 Review.
Cited by
-
From blood drops to biomarkers: a scoping review of microsampling in mass spectrometry-based proteomics.Clin Proteomics. 2025 May 18;22(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12014-025-09540-w. Clin Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 40383761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins C.J., Chang I.J., Jung S., Dayuha R., Whiteaker J.R., Segundo G.R.S., Torgerson T.R., Ochs H.D., Paulovich A.G., Hahn S.H. Rapid Multiplexed Proteomic Screening for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders from Dried Blood Spots. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:2756. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02756. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

