Repeatability and Validity of Different Methods to Determine the Anaerobic Threshold Through the Maximal Multistage Test in Male Cyclists and Triathletes
- PMID: 39846650
- PMCID: PMC11755602
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk10010009
Repeatability and Validity of Different Methods to Determine the Anaerobic Threshold Through the Maximal Multistage Test in Male Cyclists and Triathletes
Abstract
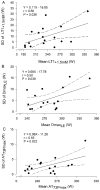
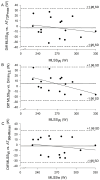
Objectives: The aim of this study was to analyze the repeatability and validity of different methods to determine the anaerobic threshold through a maximal multistage cycling test; Methods: In total, 17 male endurance-trained athletes [7 cyclists and 10 triathletes, age 33.2 ± 6.9 yr, workload at maximal lactate steady state (MLSSW) 268 ± 27 W] participated in the study. The participants performed a maximal multistage cycling test twice to analyze the repeatability of the anaerobic threshold (AT) using nine different methods. In the remaining sessions, several 20 min constant load tests were performed to determine MLSSW (gold standard); Results: The workload corresponding to 73% of the maximal power (AT73Pmax) showed the best repeatability followed by the Dmax method calculated from the blood lactate concentration ([La-]) associated with the Minimum Lactate Equivalent and final [La-] (DmaxLE). Validity analyses showed that all AT determined in the present study were strong predictors of MLSSW, however, AT73Pmax and the workloads at 1.5 mmol·L-1 above the first lactate threshold significantly underestimated MLSSW. The use of correction equations for these variables lowered their absolute mean bias to <5 W. DmaxLE and workload associated with the 86% of the maximal heart rate showed the narrowest limits of agreement to estimate MLSSW closely followed by corrected AT73Pmax; Conclusions: AT73Pmax, using the correction equation and DmaxLE, stand out as powerful predictors of MLSSW among the variables analyzed in the present study in trained cyclists or triathletes. Sports physiologists and coaches can use corrected AT73Pmax and DmaxLE to accurately assess athletes' endurance capacity and prescribe their training.
Keywords: aerobic capacity; endurance assessment; endurance performance; exercise testing; lactate threshold.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of maximal lactate steady state with anaerobic threshold determined by various methods based on graded exercise test with 3-minute stages in elite cyclists.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2020 Nov 17;12(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13102-020-00219-3. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 33292555 Free PMC article.
-
The Maximal Lactate Steady State Workload Determines Individual Swimming Performance.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 26;12:668123. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.668123. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33981254 Free PMC article.
-
Maximal lactate steady state in running mice: effect of exercise training.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Aug;34(8):760-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04635.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17600553
-
The concept of maximal lactate steady state: a bridge between biochemistry, physiology and sport science.Sports Med. 2003;33(6):407-26. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200333060-00003. Sports Med. 2003. PMID: 12744715 Review.
-
The science of cycling: physiology and training - part 1.Sports Med. 2005;35(4):285-312. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200535040-00002. Sports Med. 2005. PMID: 15831059 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

