Time Estimation Following an Exhaustive Exercise
- PMID: 39846676
- PMCID: PMC11755588
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk10010035
Time Estimation Following an Exhaustive Exercise
Abstract
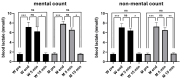
Background/Objectives: Time estimation was investigated in 24 healthy adults, including 12 women and 12 men, before and after an exhaustive exercise. Methods: We compared the ability of estimating time intervals in the range 1 to 5 s using tasks requiring mental counting and tasks that did not allow it. Time estimation and blood lactate levels were evaluated before and at the end of the exercise. Results: We found that the perception of time intervals between 1 and 5 s was affected at the end of the exercise. The observed effects, associated with a significant increase in blood lactate levels, were different in the two types of time estimation used in the present study. When participants had to evaluate the duration of the time interval using mental counting, a significant reduction in the overestimation of time made at rest was observed at the end of exercise. On the other hand, when participants had to assess the difference in duration between two events without the possibility of mental counting, a significant deterioration in performance was observed at the end of the exercise. In both cases, no differences were seen between genders. Conclusions: It could be hypothesized that an increase in blood lactate, acting as a type of physiological arousal, could contribute to the distortion of perceived time intervals. On the other hand, it does not yet seem possible to propose a model to explain the worsening of the perception of time when mental counting is not possible.
Keywords: blood lactate; exhaustive exercise; healthy adult; temporal processing; time; time estimation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kinsbourne M., Hicks R.E. The extended present: Evidence from time estimation from amnesics and normals. In: Vallar G., Shallice T., editors. Neuropsychological Impairment of Short-Term Memory. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1990. pp. 319–329.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

