Plasma Humanin and Non-Coding RNAs as Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 39846683
- PMCID: PMC11755443
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna11010005
Plasma Humanin and Non-Coding RNAs as Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study
Abstract
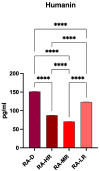
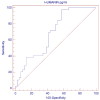
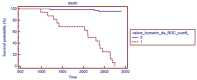
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), largely driven by peripheral endothelial dysfunction (ED). Humanin, a mitochondrial-derived peptide, has been suggested to play a protective role in endothelial function. However, the relationship between Humanin levels and ED in RA, as well as the interaction between Humanin and non-coding RNAs such as Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5, microRNA-21 (miR-21), and microRNA-103 (miR-103), remains unclear. Objective: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between circulating Humanin levels, non-coding RNAs (GAS5, miR-21, miR-103), and endothelial dysfunction (ED) in patients with RA. Additionally, we explored the correlation between Humanin expression and specific non-coding RNAs (GAS5, miR-21, and miR-103) to better understand their potential role in vascular health. Methods: Peripheral ED was assessed using flow-mediated pulse amplitude tonometry, with Ln-RHI values <0.51 indicating dysfunction. Humanin levels, GAS5, miR-21, and miR-103 were measured in RA patients. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to determine the relationship between these biomarkers and ED. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and ROC curve analysis were used to assess the prognostic value of Humanin. Results: Higher Humanin levels were significantly associated with better endothelial function (OR = 0.9774, p = 0.0196). Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that higher Humanin levels correlated with improved survival (p < 0.0001). The non-coding RNAs (GAS5, miR-21, and miR-103) did not show significant associations with ED. Conclusions: Humanin is a potential protective biomarker for endothelial dysfunction and survival in RA patients. Further research is needed to explore the interaction between Humanin and non-coding RNAs in the context of vascular health.
Keywords: biomarkers; cardiovascular risk; endothelial dysfunction; humanin; long non-coding RNA; miRNA; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Özkan U., Kakilli N., Gürdoğan M., Taştekin N., Birtane M. Rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular comorbidities. Explor. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2023;1:264–288. doi: 10.37349/emd.2023.00028. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

