ROCK Inhibitor Enhances Resilience Against Metabolic Stress Through Increasing Bioenergetic Capacity in Corneal Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 39847368
- PMCID: PMC11759620
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.51
ROCK Inhibitor Enhances Resilience Against Metabolic Stress Through Increasing Bioenergetic Capacity in Corneal Endothelial Cells
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effect of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y27632 on bioenergetic capacity and resilience of corneal endothelial cells (CECs) under metabolic stress.
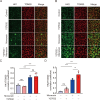
Methods: Bovine CECs (BCECs) were treated with Y27632 and subjected to bioenergetic profiling using the Seahorse XFp Analyzer. The effects on adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production through oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis were measured. BCECs were also challenged with monensin to induce metabolic stress. Cell viability, apoptosis, intracellular sodium levels, and hexokinase localization were assessed using calcein AM assay, flow cytometry, fluorescence imaging, and immunostaining, respectively.
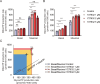
Results: Y27632 increased maximal ATP production rates via both oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis, thereby expanding the overall bioenergetic capacity in BCECs. Under monensin-induced metabolic stress, ROCK inhibitor pretreatment significantly enhanced glycolytic ATP production and reduced apoptosis compared with untreated cells. Y27632 also facilitated sodium export by increasing Na/K-ATPase activity, as evidenced by lower intracellular sodium levels. Additionally, Y27632 promoted the translocation of hexokinase 2 to mitochondria under stress conditions, thereby enhancing glycolytic capacity. The effect of Y27632 on cell viability and sodium export was abrogated when cells were forced to rely on oxidative phosphorylation in galactose media, indicating that the protective effects of Y27632 are dependent on glycolytic ATP production under monensin stress.
Conclusions: ROCK inhibitor Y27632 enhances the bioenergetic capacity of BCECs, allowing the cells to better withstand metabolic stress by rapidly generating ATP to meet increased energy demands, maintaining ion homeostasis and reducing apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures





References
-
- Huang B, Blanco G, Mercer RW, Fleming T, Pepose JS.. Human corneal endothelial cell expression of Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase isoforms. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121: 840–845. - PubMed
-
- Edelhauser HF. The balance between corneal transparency and edema: the Proctor lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47: 1755–1767. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

