Construction of an lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network to investigate the inflammatory regulatory mechanisms of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 39847586
- PMCID: PMC11756804
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317710
Construction of an lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network to investigate the inflammatory regulatory mechanisms of ischemic stroke
Abstract
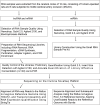
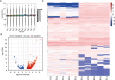
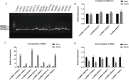
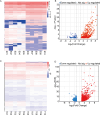
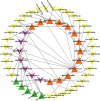
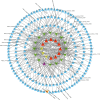
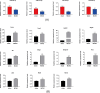
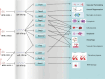
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are among the most abundant types of non-coding RNAs in the genome and exhibit particularly high expression levels in the brain, where they play crucial roles in various neurophysiological and neuropathological processes. Although ischemic stroke is a complex multifactorial disease, the involvement of brain-derived lncRNAs in its intricate regulatory networks remains inadequately understood. In this study, we established a cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury model using middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in male Sprague-Dawley rats. High-throughput sequencing was performed to profile the expression of cortical lncRNAs post-stroke, with subsequent validation using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR. Among the 31,183 lncRNAs detected in the rat cerebral cortex, 551 were differentially expressed between the MCAO and sham-operated groups in the ipsilateral cortex (fold change ≥2.0, P < 0.05). An integrated analysis of the 20 most abundant and significantly differentially expressed lncRNAs (DELs) identified 25 core cytoplasmic DELs, which were used to construct an interaction network based on their targeting relationships. This led to the establishment of a comprehensive lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network comprising 12 lncRNAs, 16 sponge miRNAs, and 191 target mRNAs. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses revealed that differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs) were significantly enriched in stroke-related pathways. Our analysis predicted four key lncRNAs, four miRNAs, and eleven crucial mRNAs involved in post-transcriptional regulation through competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanisms. These molecules were shown to participate extensively in post-stroke processes, including angiogenesis, axonal regeneration, inflammatory responses, microglial activation, blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, and thrombocytopenia. These findings highlight the role of lncRNAs as multi-level regulators in the complex network of post-stroke mechanisms, providing novel insights into the pathophysiological processes of stroke.
Copyright: © 2025 Xu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49(3):e46–110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

