Improving Mental Health and Well-Being Through the Paradym App: Quantitative Study of Real-World Data
- PMID: 39848610
- PMCID: PMC11803330
- DOI: 10.2196/68031
Improving Mental Health and Well-Being Through the Paradym App: Quantitative Study of Real-World Data
Abstract
Background: With growing evidence suggesting that levels of emotional well-being have been decreasing globally over the past few years, demand for easily accessible, convenient, and affordable well-being and mental health support has increased. Although mental health apps designed to tackle this demand by targeting diagnosed conditions have been shown to be beneficial, less research has focused on apps aiming to improve emotional well-being. There is also a dearth of research on well-being apps structured around users' lived experiences and emotional patterns and a lack of integration of real-world evidence of app usage. Thus, the potential benefits of these apps need to be evaluated using robust real-world data.
Objective: This study aimed to explore usage patterns and preliminary outcomes related to mental health and well-being among users of an app (Paradym; Paradym Ltd) designed to promote emotional well-being and positive mental health.
Methods: This is a pre-post, single-arm evaluation of real-world data provided by users of the Paradym app. Data were provided as part of optional built-in self-assessments that users completed to test their levels of depression (Patient Health Questionnaire-9), anxiety (Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire-7), life satisfaction (Satisfaction With Life Scale), and overall well-being (World Health Organization-5 Well-Being Index) when they first started using the app and at regular intervals following initial usage. Usage patterns, including the number of assessments completed and the length of time between assessments, were recorded. Data were analyzed using within-subjects t tests, and Cohen d estimates were used to measure effect sizes.
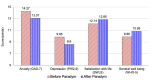
Results: A total of 3237 app users completed at least 1 self-assessment, and 787 users completed a follow-up assessment. The sample was diverse, with 2000 users (61.8%) being located outside of the United States. At baseline, many users reported experiencing strong feelings of burnout (677/1627, 41.6%), strong insecurities (73/211, 34.6%), and low levels of thriving (140/260, 53.8%). Users also experienced symptoms of depression (mean 9.85, SD 5.55) and anxiety (mean 14.27, SD 6.77) and reported low levels of life satisfaction (mean 12.14, SD 7.42) and general well-being (mean 9.88, SD 5.51). On average, users had been using the app for 74 days when they completed a follow-up assessment. Following app usage, small but significant improvements were reported across all outcomes of interest, with anxiety and depression scores improving by 1.20 and 1.26 points on average, respectively, and life satisfaction and well-being scores improving by 0.71 and 0.97 points, respectively.
Conclusions: This real-world data analysis and evaluation provided positive preliminary evidence for the Paradym app's effectiveness in improving mental health and well-being, supporting its use as a scalable intervention for emotional well-being, with potential applications across diverse populations and settings, and encourages the use of built-in assessments in mental health app research.
Keywords: apps; awareness; emotional well-being; formative; mental health; mobile phone; pre-post; quantitative data; quantitative evaluation; real-world data; single arm; well-being.
©Athina Marina Metaxa, Shaun Liverpool, Mia Eisenstadt, John Pollard, Courtney Carlsson. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 23.01.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: CC is the founder and Chief Executive Officer of Paradym Ltd, and JP is the Head of Development lead at Paradym Ltd. AMM, ME, and SL were commissioned as external consultants during the analysis and write-up of this evaluation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acceptability, Engagement, and Exploratory Outcomes of an Emotional Well-being App: Mixed Methods Preliminary Evaluation and Descriptive Analysis.JMIR Form Res. 2021 Nov 1;5(11):e31064. doi: 10.2196/31064. JMIR Form Res. 2021. PMID: 34569466 Free PMC article.
-
An Empathy-Driven, Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent (Wysa) for Digital Mental Well-Being: Real-World Data Evaluation Mixed-Methods Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Nov 23;6(11):e12106. doi: 10.2196/12106. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018. PMID: 30470676 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Clear Fear Smartphone App for Young People Experiencing Anxiety: Uncontrolled Pre- and Post-Follow-Up Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Feb 28;9:e55603. doi: 10.2196/55603. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40053764 Free PMC article.
-
When and Why Adults Abandon Lifestyle Behavior and Mental Health Mobile Apps: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Dec 18;26:e56897. doi: 10.2196/56897. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39693620 Free PMC article.
-
Scope, Characteristics, Behavior Change Techniques, and Quality of Conversational Agents for Mental Health and Well-Being: Systematic Assessment of Apps.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 18;25:e45984. doi: 10.2196/45984. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37463036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agteren J, Iasiello M. Advancing our understanding of mental well-being and mental health: the call to embrace complexity over simplification. Australian Psychologist. 2021;55(4):307–316. doi: 10.1111/ap.12440. - DOI
-
- Huppert F. Psychological well‐being: evidence regarding its causes and consequences. Applied Psych Health & Well. 2009;1(2):137–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-0854.2009.01008.x. - DOI
-
- Kaufman KR, Petkova E, Bhui KS, Schulze TG. A global needs assessment in times of a global crisis: world psychiatry response to the COVID-19 pandemic. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(3):e48. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2020.25. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32250235 S2056472420000253 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salari N, Hosseinian-Far A, Jalali R, Vaisi-Raygani A, Rasoulpoor S, Mohammadi M, Rasoulpoor S, Khaledi-Paveh B. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Health. 2020;16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w. https://globalizationandhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12992... 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

