Systemic IFN-I combined with topical TLR7/8 agonists promotes distant tumor suppression by c-Jun-dependent IL-12 expression in dendritic cells
- PMID: 39849091
- PMCID: PMC11779648
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-024-00889-9
Systemic IFN-I combined with topical TLR7/8 agonists promotes distant tumor suppression by c-Jun-dependent IL-12 expression in dendritic cells
Abstract
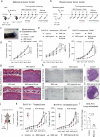
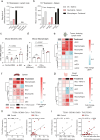
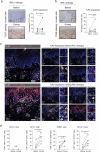
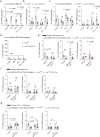
Dendritic cell (DC) activation by pattern recognition receptors like Toll-like-receptors (TLRs) is crucial for cancer immunotherapies. Here, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the TLR7/8 agonist imiquimod (IMQ) in treating both local tumors and distant metastases. Administered orally, IMQ activates plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) to produce systemic type I interferons (IFN-I) required for TLR7/8 upregulation in DCs and macrophages, sensitizing them to topical IMQ treatment, which is essential for therapeutic efficacy. The mechanism involves c-Jun/AP-1 mediating TLR7/8 signaling in IFN-I-primed DCs, upregulating the pDC-recruiting chemokine CCL2 and the anti-angiogenic cytokine interleukin-12, which suppresses VEGF-A production leading to tumor necrosis and regression. Combining topical and systemic IMQ or IFN-I generates a CD8+ T cell-dependent response at metastatic sites, reinforced by PD-1 blockade, leading to long-lasting memory. Analysis of cohorts of patients with melanoma demonstrates DC-specific TLR7/8 upregulation by IFN-I, supporting the translational potential of combining systemic IFN-I and topical IMQ to improve immunotherapy of topically accessible tumors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Pasare, C. & Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.560, 11–18 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Hemmi, H. et al. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol.3, 196–200 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Hadley, G., Derry, S. & Moore, R. A. Imiquimod for actinic keratosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Investig. Dermatol.126, 1251–1255 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 694883/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- W1212/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
- DOC 32-B28/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

