Selective arm-usage of pre-miR-1307 dysregulates angiogenesis and affects breast cancer aggressiveness
- PMID: 39849498
- PMCID: PMC11756181
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-025-02133-x
Selective arm-usage of pre-miR-1307 dysregulates angiogenesis and affects breast cancer aggressiveness
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women. Deregulation of miRNAs is frequently observed in breast cancer and affects tumor biology. A pre-miRNA, such as pre-miR-1307, gives rise to several mature miRNA molecules with distinct functions. However, the impact of global deregulation of pre-miR-1307 and its individual mature miRNAs in breast cancer has not been investigated in breast cancer, yet.
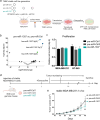
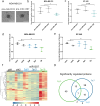
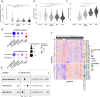
Results: Here, we found significant upregulation of three mature miRNA species derived from pre-miR-1307 in human breast cancer tissue. Surprisingly, the overexpression of pre-miR-1307 in breast cancer cell lines resulted in reduced xenograft growth and impaired angiogenesis. Mechanistically, overexpression of miR-1307-5p altered the secretome of breast cancer cells and reduced endothelial cell sprouting. Consistently, expression of miR-1307-5p was inversely correlated with endothelial cell fractions in human breast tumors pointing at an anti-angiogenic role of miR-1307-5p. Importantly, the arm usage of miR-1307 and other miRNAs was highly correlated, which suggests an undefined common regulatory mechanism.
Conclusions: In summary, miR-1307-5p reduces angiogenesis in breast cancer, thereby antagonizing the oncogenic effects of miR-1307-3p. Our results emphasize the importance of future research on the regulation of miRNA arm selection in cancer. The underlying mechanisms might inspire new therapeutic strategies aimed at shifting the balance towards tumor-suppressive miRNA species.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Breast cancer; IsomiRs; Metastasis; Selective arm-usage of miRNA; miR-1307; miRNA arm switch; miRNAs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Weizmann Institute of Science (experiments with NOG mice) and by the local regulatory authorities (regional council, Karlsruhe, Germany under reference code G288/14; experiments with NSG mice). No human subjects were involved in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiR-5586-5p Suppresses Hypoxia-induced Angiogenesis Through Multiple Targeting of HIF-1α, HBEGF and ADAM17 in Breast Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2025 Feb;45(2):473-489. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17437. Anticancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39890164
-
5'isomiR-183-5p|+2 elicits tumor suppressor activity in a negative feedback loop with E2F1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 2;41(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02380-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35655310 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenic role of miR-20a in breast cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 4;13(4):e0194638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194638. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29617404 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-205-5p inhibits the growth and migration of breast cancer through targeting Wnt/β-catenin co-receptor LRP6 and interacting with lncRNAs.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2117-2129. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05136-4. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39461917 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–52. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

